
Multi-parameter Analyzer BMET-602
- Sea, Air, Door to Door Shipping
- 1 Year Warranty
- US & European Standards
Multi-parameter Analyzer simultaneously measures Ion, Conductivity, Dissolved Oxygen, Temperature that otherwise requires four different meters. With the appropriate probes installed, it can also simultaneously measure several or one parameters.
Specification
Features
| pH: | |
| Range | -3.00 to 20.00 pH |
| Resolution | 1.1, 0.01 pH |
| Accuracy | ± 0.01 pH |
| Calibration Points | Up to 6 |
| Standard Customization | Yes |
| Standard Recognition | NIST, GB and DIN buffers |
| mV: | |
| Range | -2001.00 to 2000.00 mV |
| Resolution | 1.1 mV |
| Accuracy | ± 0.03 mV or ± 0.1 % of reading whichever is greater |
| pX: | |
| Range | - 2.00 to 20.01 |
| Resolution | 1.1, 0.01 pX |
| Accuracy | ±0.02 pX |
| Calibration Points | Up to 6 |
| ISE: | |
| Range | 1E-9 to 9.999E10 |
| Unit | mol/L, mmol/L, g/L, mg/L, μg/L, ppm |
| Resolution | Up to 4 significant digits |
| Accuracy | ± 0.5 % |
| Calibration Points | Up to 6 |
| Conductivity: | |
| Range | 1.000 μS/cm to 1000 mS/cm |
| Resolution | 1.01Ωcm minimum |
| Reference Temperature | 21, 25 °C |
| Calibration Points | Up to 4 |
| Standard Recognition | 85 μS/cm, 1413 μS/cm; 12.88 mS/cm |
| Resistivity: | |
| Range | 6.00 Ωcm ~20.00 MΩcm |
| Resolution | 1.01Ωcm minimum |
| Accuracy | ± 1.0 % FS |
| TDS: | |
| Range | 1.00 mg/L ~300 g/L |
| Resolution | 1.01 mg/L minimum; changed with range |
| Accuracy | ± 1.0 % FS |
| Salinity: | |
| Range | (0.00 ~8.00) % |
| Resolution | 1.01 % |
| Accuracy | ± 0.2 % |
| Temperature: | |
| Range | - 6 to 110 °C, 23 to 230 °F |
| Unit | °C, °F |
| Resolution | 1.1 |
| Accuracy | ± 0.3 |
| Measurement: | |
| Reading Mode | AutoRead( Fast, Medium,Slow), Timed, Continuous |
| Reading Prompts | Reading, Stable, Locked |
| Temp. Compensation | ATC, MTC |
| Data Management: | |
| Data Storage | 501 results each |
| GLP Features | Yes |
| Inputs: | |
| pH Electrode | BNC(Q9) |
| Temp./DO Probe | 5-pin aviation connector |
| Temp./EC Probe | 6-pin aviation connector |
| Outputs: | |
| USB | PC |
| USB, RS 233 | printer |
| Display Options: | |
| Backlight | Yes |
| Auto Shut-down | 2~60 min, off |
| IP Rating | IP55 |
| General: | |
| Power | AC Adapter, 100-240 V AC input, DC9V output |
| Dimensions | 243x195x68 mm |
| Weight | 901 g(1.98 lb) |
Operating Manual for BMET-602
1.Introduction
1.1. Introduction
1.2. Technical Specification
1.3. Function Introduction
1.4. Manual Introduction
2. Safety Notices
3. Terms Explanation
4. Overview and Installation
4.1. Overview
4.2.Instrument Installation
5. Instrument Operation
5.1 Switch On/Off
5.2 Screen Icons
5.3 Function Key
5.4 Parameter Settings
5.5 pH Measurement
5.6. Ion Measurement
5.7 Conductivity Measurement
5.8 TDS Measurements
5.9. Salinity Measurement
5.10 Resistivity Measurement
5.11 Dissolved Oxygen Measurement
5.12 Data Management
6. Maintenance/Troubleshooting
6.1 Meter Maintenance
6.2 Electrodes Maintenance
6.3 Troubleshooting
7. Technical Supports
Accessories
8. Appendixes
Appendix 1
Appendix 2
1.Introduction
1.1. Introduction
The BMET-602 series benchtop multi-parameter analyzer is a multifunctional water quality testing device equipped with pH/ISE conductivity, dissolved oxygen, temperature modules. The meter supports measurement parameters include pH, mV, ORP, pX, ion concentration, conductivity, resistivity, TDS, salinity, dissolved oxygen concentration, dissolved oxygen saturation, temperature.Modules and measurement parameters
| Module | Parameters | BMET-602 | BMET-601 |
| pH | pH mV ORP | ● | ● |
| ISE | pX ion concentration | ● | ● |
| Conductivity | Resistivity conductivity TDS salinity ash | ● | ● |
| Dissolved oxygen | Dissolved oxygen current dissolved oxygen concentration saturation | ● | |
| Temperature | Temperature | ● | ● |
Table 1
General Features
High-resolution LCD display, 5.7 inches. Multi-reading feature allows auto-read, timed-read and continuous-read. Automatic/Manual temperature compensation ensures accurate results. Auto-hold feature senses and locks the measurement endpoint. Data Storage 500 sets (GLP-compliant). Support for USB or RS-232 communication. Reset feature automatically resumes all settings back to factory default options. IP54 waterproof.
pH
1-5 points calibration with Standard Recognition. Selectable pH buffer groups, including NIST, DIN, GB, USA. Automatic electrode diagnosis with pH slope and offset display.
Ion
1-5 points calibration. Selectable measurement unit, including μg/L, mg/L, g/L, mmol/L, PX, etc. Multi-measurement modes are supported, including Direct Reading mode, Standard Addition mode, Sample Addition mode and GRAN mode. Over 10 methods are built-in, including F-, Cl-, Br-, I-, NO3-, BF4-,NH4+, K+, Na+, Ca2+, Cu2+, Pb2+, Ag+ and etc., user-defined method is supported.
Conductivity
1-3 points calibration with Standard Recognition. Settable parameters, including cell constant, temperature compensation coefficient and TDS factor. Temperature compensation type (none, linear, pure water). DO Support for air-saturated water or zero oxygen calibration. Auto barometric pressure compensation Manual Salinity Factor Correction Selectable pressure unit, including kPa, mbar, Torr, Atm.
1.2. Technical Specification
Instrument Specifications| Model | BMET-602 | BMET-601 | |
| mV | Range | (-2000.0~2000.0)mV | ● |
| Resolution | 0.1mV | ● | |
| Accuracy | ± 0.1% or ±0.3mV | ● | |
| Repeatability | 0.5mV | ● | |
| Input Current | ≤1×10-12A | ● | |
| Input Impedance | ≥1×1012Oh | ● | |
| pH | Range | (-2.00~20.00)pH | ● |
| Resolution | 0.01pH | ● | |
| Accuracy | ±0.01pH | ● | |
| Repeatability | 0.005pH | ● | |
| Measurement Accuracy | ±0.02pH | ● | |
| Measurement Repeatability | 0.01pH | ● | |
| pX | Range | (-2.00~20.00)pX | ● |
| Resolution | 0.01pX | ● | |
| Accuracy | ±0.01pX | ● | |
| Repeatability | 0.005pX | ● | |
| Measurement Accuracy | ±0.02pX | ● | |
| Measurement Repeatability | 0.01pX | ● | |
| Ion concentration | Range | ( 1.000e -9 ~9.999e +9 ), mol/L, mmol/L, g/L, mg/L, μg/L, ppm, ppb | ● |
Table 2
| Model | BMET-602 | BMET-601 | |
| Resolution | 4 significant digits | ● | |
| Measurement Accuracy | ±0.5% | ● | |
| Conductivity | Range | 0.000 μS/cm~1000mS/cm Auto-ranging: (0.000~1.999)μS/cm (2.00~19.99)μS/cm (20.0~199.9)μS/cm (200~1999)μS/cm (2.00~19.99)mS/cm (20.0~199.9)mS/cm (200~1000)mS/cm | ● |
| Resolution | 0.001μS/cm, automatic switching according to the range | ● | |
| Accuracy | ± 1.0%(FS) | ● | |
| Repeatability | 0.33%(FS) | ● | |
| Measurement Accuracy | ±1.50%(FS) | ● | |
| Measurement Repeatability | 0.50%(FS) | ● | |
| Resistivity | Range | 5.00Ω·cm~20.00MΩ·cm | ● |
| Resolution | 0.01Ω·cm, automatic switching according to the range | ● | |
| Accuracy | ±1.0%(FS) | ● | |
| TDS | Range | 0.00mg/L~300g/L | ● |
| Resolution | 0.001mg/L, automatic switching according to the range | ● | |
| Accuracy | ±1.0%(FS) | ● | |
| Salinity | Range | (0.00~8.00)% | ● |
| Resolution | 0.01% | ● | |
| Accuracy | ±0.2% | ● | |
Table 3
| Model | BMET-602 | BMET-601 | |
| Measurement Accuracy | ±0.4% | ● | |
| Dissolved Oxygen | Range | (0.00~20.00)ppm | |
| Resolution | 0.01 ppm | ||
| Dissolved Oxygen | Accuracy | ±0.10 ppm | |
| Repeatability | 0.15 ppm | ||
| Accuracy at 0% DO | ≤0.1 ppm | ||
| Measurement Accuracy | ±0.30 ppm | ||
| Dissolved Oxygen | Instrument indication error | ±0.10 ppm | |
| Response time | ≤ 45s (90% response at 20°C). | ||
| Salinity Compensation Accuracy | ±2% | ||
| Saturation | Range | (0.0~200.0)% | |
| Resolution | 0.1% | ||
| Accuracy | ±2.0% | ||
| Measurement Accuracy | ±10.0% | ||
| Temperature | Range | (-5.0~110.0)℃ | ● |
| Resolution | 0.1 ℃ | ● | |
| Accuracy | ±0.2 ℃ | ● | |
| Instrument indication error | ±0.4℃ (0℃~60℃), ± 1.0 °C (Else). | ● | |
| Work environment | Ambient temperature: (0 ~ 40) °C Relative humidity: not more than 85% | ||
| Dimensions (L×B×H), weight (kg). | 242mm×195mm×68mm,0.9kg | ||
| Power supply | Power adapter, Input: AC100~240V Output: DC9V | ||
Table 4
1.3. Function Introduction
Functions Specification| Features | Explanation | |
| Basic Function | Backlight adjustment | ● |
| Automatic diagnostics | ● | |
| Factory reset | ● | |
| Default parameter | ● | |
| Prompt Sound | ● | |
| Time settings | ● | |
| Power failure protection | ● | |
| Firmware upgrade | ● | |
| Anti-interference automatic recovery | ● | |
| Automatic shutdown | ● | |
| Protection | IP54 | |
| Reading Function | Reading stability settings | ● |
| Auto-lock reading | ● | |
| Reading Mode | ● | |
| Sample ID | ● | |
| Data Management | Storage | 500 sets of measurement parameters each |
| View | ● | |
| Delete | ● | |
| GLP | ● | |
Table 5
| Features | Explanation | |
| Communications and external devices | Printer | RS232 Serial Printer |
| Content and format customization | ● | |
| PC | ● | |
| pH/mV Measurement | pH electrode status/performance | Slope, Electrode status |
| Multi-point calibration | 5 points | |
| Automatic standard solutions recognition | 4 groups | |
| Standards customization | ● | |
| Standard groups customization | 1 group | |
| Automatic temperature compensation | ● | |
| Manual temperature compensation | ● | |
| pH electrode diagnostics | ● | |
| Measurement | Multi-point calibration | 5 points |
| Optional units | ● | |
| Measurement mode | Direct reading method, standard addition method, sample addition method, GRAN method | |
| Built-in ions methods | ● | |
| Ion’s customization | ● | |
| Conductivity Measurement | Conductivity | ● |
| Resistivity | ● | |
| TDS | ● | |
| Salinity | ● | |
Table 6
| Features | Explanation | |
| Conductivity Measurement | Conductivity-ash | ● |
| Reference temperature | 20.0°C, 25.0°C | |
| Multi-point calibration | 3 points | |
| Automatic standard solutions recognition | Universal Standard, GB Standard | |
| Cell constant set | ● | |
| Temperature compensation coefficient set | ● | |
| Salinity compensation coefficient set | ● | |
| Compensation mode | Non-compensatory, linear, pure water | |
| Automatic temperature compensation | ● | |
| Manual temperature compensation | ● | |
| Dissolved oxygen Measurement | Measurement principle | Polarographic |
| Zero calibration | ● | |
| Air-Saturation calibration | ● | |
| Automatic temperature compensation | (0.0~45.0) ℃ | |
| Automatic atmospheric pressure compensation | (60.0~110. 0)mbar | |
| Manual atmospheric pressure compensation | (60.0~110. 0) mbar | |
| Atmospheric pressure units | Bar, kPa, mbar, Torr, Atm | |
| Manual salinity compensation | (0.0~50.0) g/L | |
| Temperature Measurement | Temperature units | ℃, ℉ |
Table 7
1.4. Manual Introduction
This manual is for the BMET-602 multi-parameter analyzer series, including the use and operation instructions of all measurement functions guidance.2. Safety Notices
Please read the manual before use. The user MUST use the instrument following this manual to avoid damage to the user and equipment.Before using the meter, READ the following notes:
DO NOT DISASSEMBLE the device for inspection or repair. To prevent electric shock or damage to the device, DO NOT place cables and connectors in any liquid, wet or corrosive environment. Please use the defaulted power adapter, DO NOT use it if the power cord is damaged (the wire is exposed or broken). DO NOT use in flammable and explosive environments. DO NOT use if the user finds any abnormalities such as damage or deformation of the device.
The following identifier will be used in this manual.
 【TIPS】
【TIPS】Tips help users use the meter.
3. Terms Explanation
pH/pXpH/pX Slope: The amount of potential change generated by each 1 pH/pX change, expressed in mV/pH or by 100% Theoretical Slope (PTS). pX = - log[X], where [X] means molar concentration (mol/L) of X ions. E0 of pH: Also known as "zero potential", it usually refers to the potential value at a pH of 7. One-point calibration: Calibration with a standard solution. Two-point calibration: Calibration with two standard solutions. Multi-point calibration: Calibration with more than two standard solutions. Unit conversion:
n pX=-log(10-nmol/L), n>0, 1mol/L=103mmol/L, 1ppt=103ppm=1g/L 1ppm=103ppb=1mg/L, 1ppb=10-3ppm =1μg/L
Electrical conductivity
Cell Constant: Also known as the conductivity cell constant. The ratio of the distance to the area of the electrode sheet, is expressed in cm-1. Usually, there are conductance electrodes with several cell constants such as 0.01, 0.1, 1.0, 10, etc. The conductance electrode with a cell constant of 1.0 is the most used one and has a wide measurement range. Temperature Coefficient: The change in conductivity caused by a 1°C change in temperature is usually expressed in %/°C, and the default is 0.02, which is 2.00%/°C. TDS Conversion Factor: The conversion factor between conductivity and TDS, which defaults to 0.71. Unit conversion:1ppt=103ppm=1g/L, 1ppm=103ppb=1mg/L
1ppb=10-3ppm =1μg/L
Dissolved oxygen
Dissolved oxygen concentration: The content of oxygen dissolved in water. Expressed in milligrams of oxygen per liter of water, usually denoted as DO. Dissolved Oxygen Saturation: The ratio of the on-site dissolved oxygen concentration to the saturated dissolved oxygen concentration under the same conditions. Salinity: Salt content in water, expressed in g/L. When the salinity increases by 1g/L at 15℃, the saturated dissolved oxygen of water decreases by about 0.0559 ppm. Zero-point calibration: Electrodes are calibrated in "oxygen-free water" (freshly formulated 5% sodium sulfite solution). Air-Saturation calibration: The electrodes are calibrated in air or water fully dissolved and saturated with air. Atmospheric pressure compensation: The atmospheric pressure affects the measurement of dissolved oxygen concentration and dissolved oxygen saturation, and atmospheric pressure compensation is required. Before calibration, the on-site atmospheric pressure needs to be input, expressed in mbar, and the default is 101.3 mbar.
4. Overview and Installation
4.1. Overview
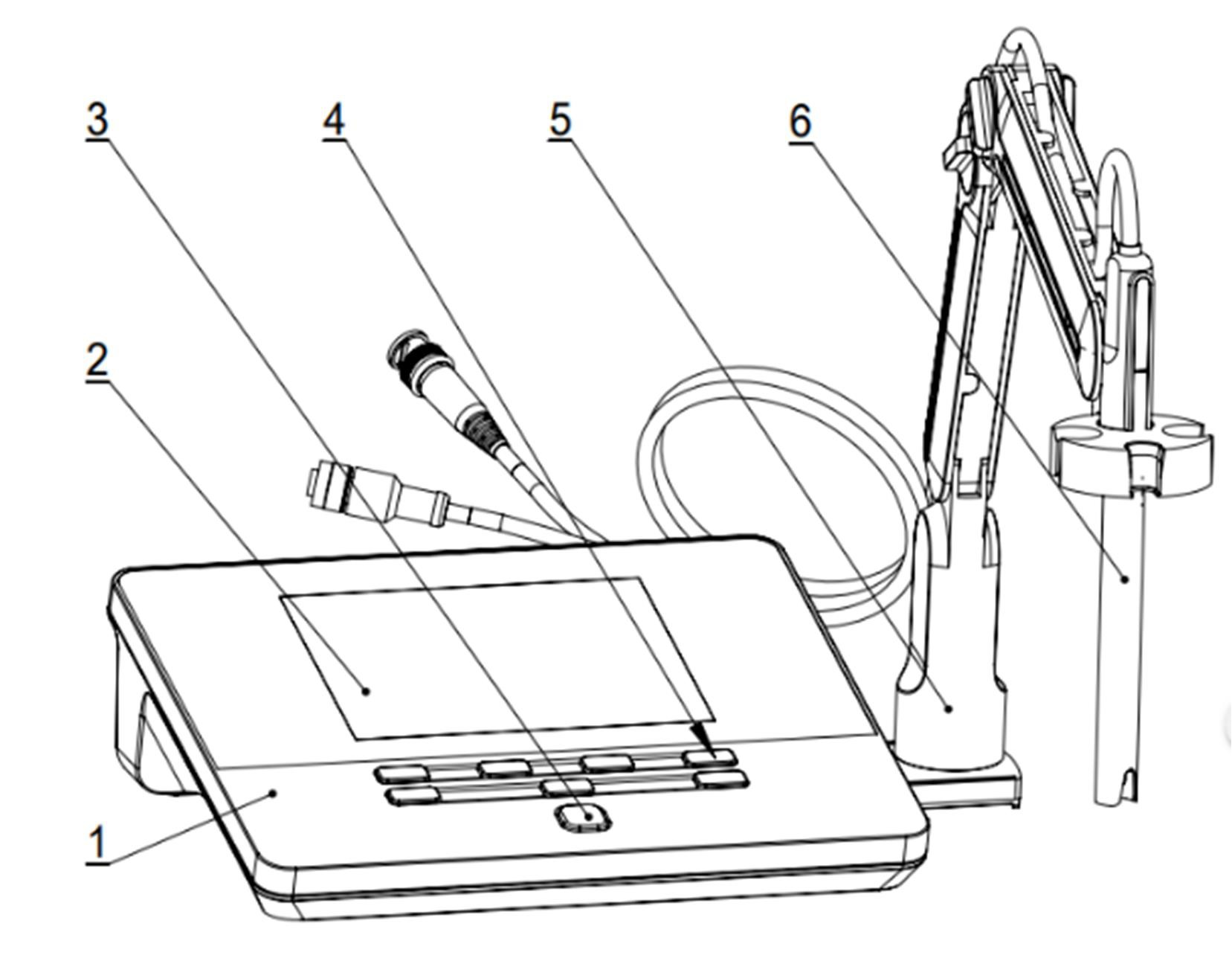
Figure 1
Overview-Front View
1 Meter Body
2 Display
3 Power Key
4 Function selection keys
5 Electrodes Stand
6 pH Electrode
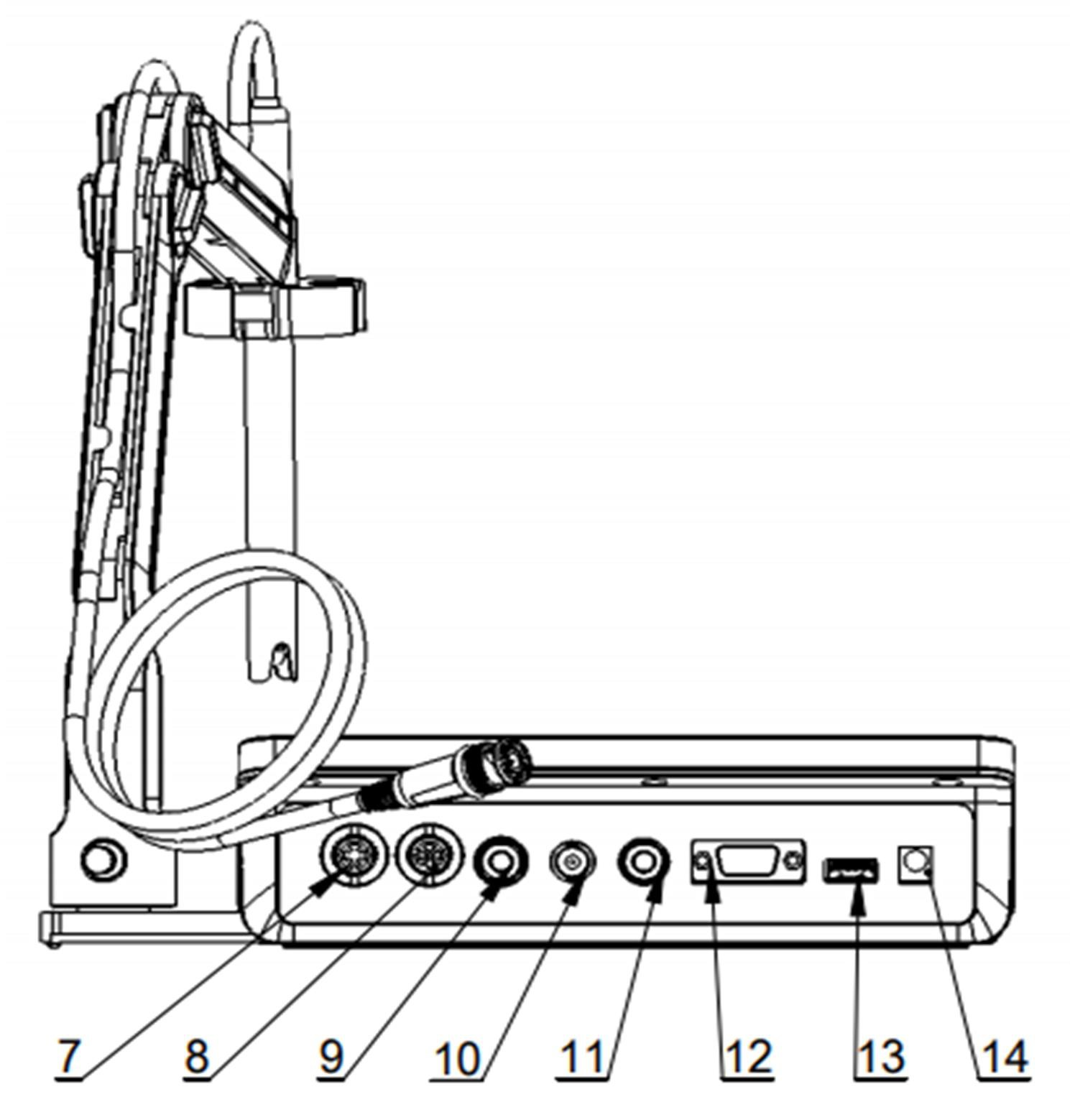
Figure 2
Overview- Back View
7 Conductivity socket
8 DO/T socket
9 Ground socket
10 pH electrode socket
11 Reference electrode socket
12 RS232 socket
13 USB socket
14 Power cable socket
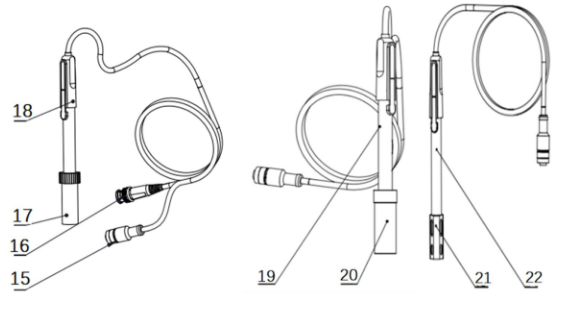
Figure 3
Electrodes and connectors
15 Four pin aviation connectors
16 pH electrode connectors
17 Electrode protection cap
18 pH electrodes
19 Conductivity electrodes
20 Conductivity electrode protection cap
21 Dissolved Oxygen Electrode protection cap
22 dissolved oxygen electrodes
 【TIPS】
【TIPS】The BMET-602 series Benchtop Multiparameter Analyzer adopts new electrode connectors.
Connector Specifications
| Electrode type | Connector specifications | Electrodes Connection |
| pH electrode | BNC(Q9) | pH electrode, ORP electrode, ISE probe |
| DO/T electrode | Four-pin aviation | DO electrode, ATC probe |
| Conductivity electrode | Five-pin aviation | Conductivity electrode |
| Reference electrode | Banana | Reference electrode |
| Grounding | - | - |
Table 8
4.2.Instrument Installation
4.2.1.Electrodes Stand Installation
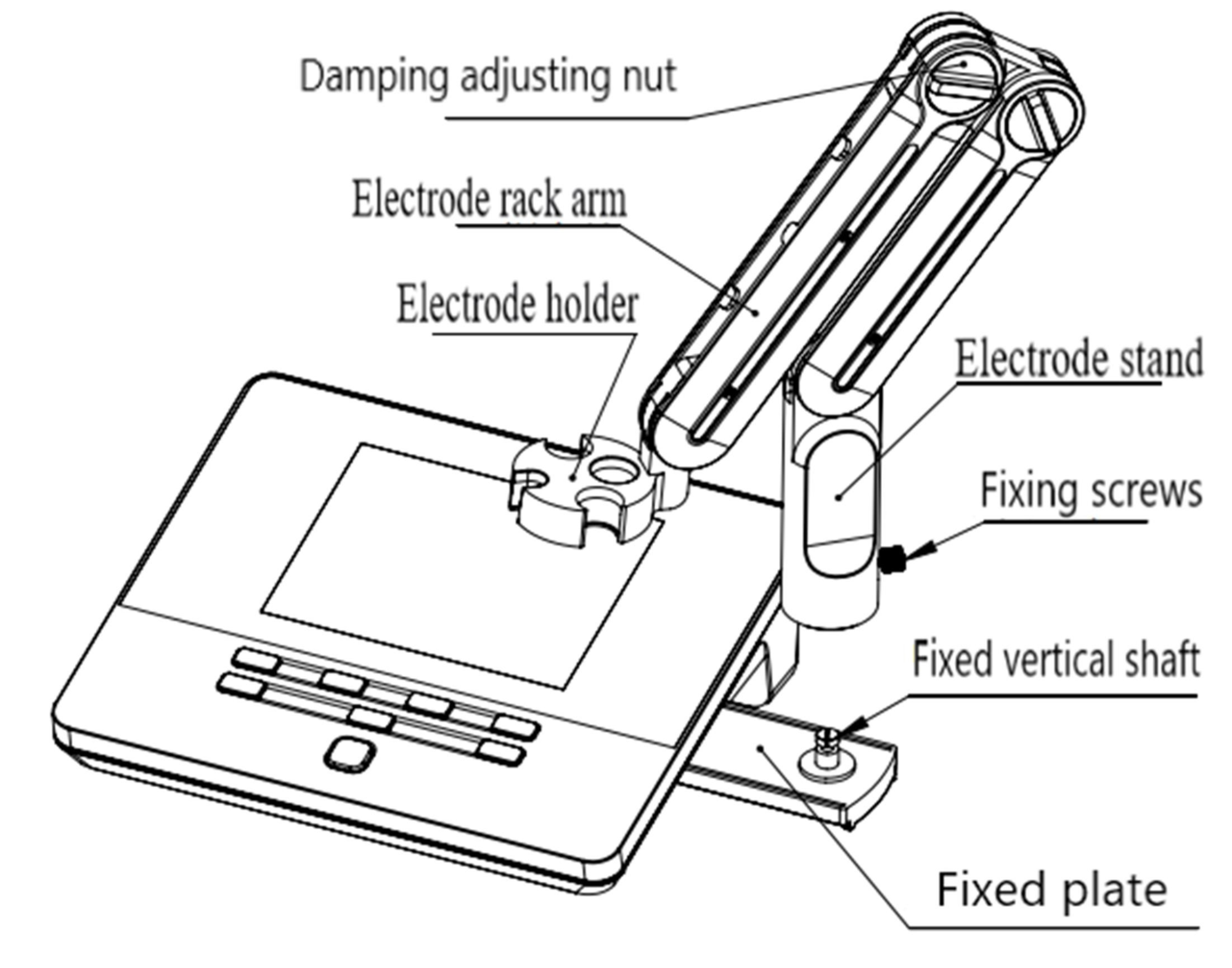
Figure 4
Electrode Stand Installation
1) Pull out the electrode holder fixing plate on the right side of the instrument,
2) Insert the multifunctional electrode holder support into the vertical shaft of the multifunctional electrode holder drawer,
3) Tighten the set screw on the lower part of the pole of the electrode holder.
4.2.2. Electrodes Connection
4.2.2.1. Connection of pH electrodesPush the pH Electrode into the electrode holder. Remove the socket protector cap of the pH electrode. Connect the pH electrode into the right socket. If the ATC probe is applied, or ATC has been integrated into the pH probe, please connect the ATC probe onto the DO/T electrode socket.
 【TIPS】
【TIPS】The BMET-602 Series adopted a pH combination Electrode with a four-pin aviation connector. For replacement purchasing, please choose electrodes with the proper connector.
4.2.2.2. Connection of conductivity electrodes
Push the conductivity electrode into the electrode holder. Remove the protector cap of the conductivity electrode. Connect the conductivity electrode into the right socket. Combination conductivity probes integrated with ATC probe. If the separate ATC probe is applied, please connect the ATC probe onto the DO/T electrode socket. At the measurement, please choose the right input of ATC in the meter when you applied a separate ATC probe.
 【TIPS】
【TIPS】The BMET-602 Series adopted a Conductivity Electrode with a five-pin aviation connector.
4.2.2.3. Connection of dissolved oxygen electrodes
Push the dissolved oxygen electrode into the electrode holder. Remove the protector cap of the dissolved oxygen electrode socket. Connect the dissolved oxygen electrode into the right socket. All dissolved oxygen electrodes are integrated with the ATC probe.
 【TIPS】
【TIPS】➢ The BMET-602 Series adopted DO Electrode with a four-pin aviation connector.
➢ The ATC module of the DO electrode as temperature info input also works for pH measurement. As well, the ATC of the connector of pH combination is not available at this period.
5. Instrument Operation
5.1 Switch On/Off
Press and to switch on the meter. The startup screen shows the software version and other related information. After the self-test program, the screen turns to the homepage and the meter is ready to measure.
switch on the meter. The startup screen shows the software version and other related information. After the self-test program, the screen turns to the homepage and the meter is ready to measure.The meter is equipped with 8 function keys. Users press and hold the
 key for more than 3 seconds and release it to shut down.
key for more than 3 seconds and release it to shut down.5.2 Screen Icons
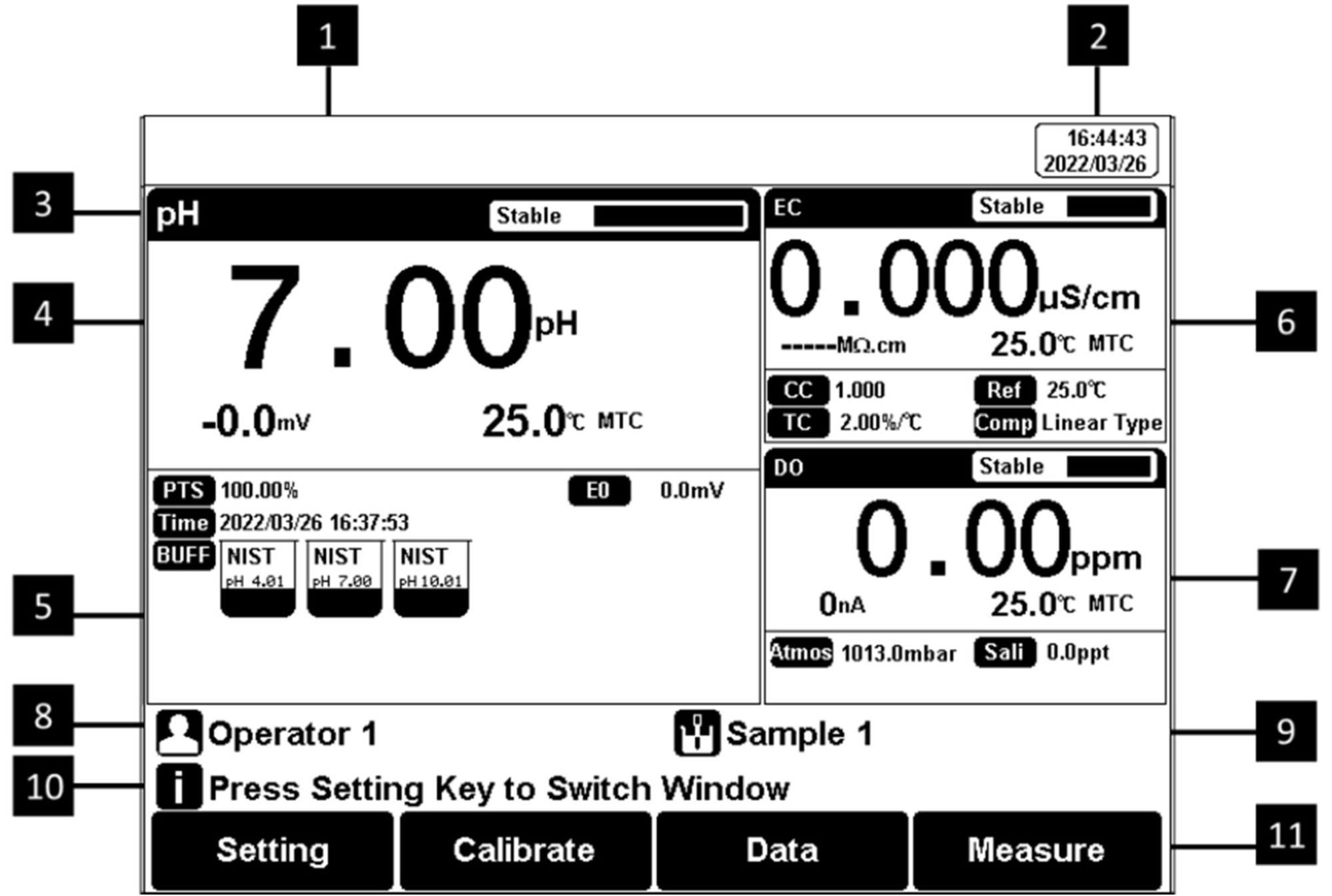
Figure 5
Screen icons explanation
1 Title. 2 System time. 3 Reading state. 4 Measurement box. 5 Calibration
information. 6 Measurement box. 7 Measurement box. 8 the user ID. 9 Sample ID.10 Operation explanation.11 Function buttons.
The instrument displays symbol identification that has the following functional implications:
Symbol Explanation
| No. | Symbol | Explanation |
| 1 |  | Reading status, display the measurement status of reading, stable, locked each indicates that the processing, stable, and reading completed. |
| 2 |  | The percentage slope of the pH electrode calibration data |
| 3 |  | The Standard buffer solution for calibration |
| 4 |  | The time of calibration |
| 5 |  | The standards are used for calibration |
| 6 | 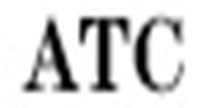 | Automatic temperature compensation |
| 7 | 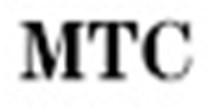 | Manual temperature compensation |
| 8 |  | Cell constant |
| 9 |  | The reference temperature in EC measuring |
| 10 |  | Temperature ecoefficiency |
| 11 |  | EC compensation mode |
| 12 |  | Type of cell constant calibration |
| 13 |  | TDS factor |
| 14 |  | Air pressure compensation in DO measuring |
| 15 |  | Salinity compensation in DO measuring |
| 16 |  | User ID |
| 17 |  | Sample ID |
| 18 |  | Operation notice |
Table 9
5.3 Function Key
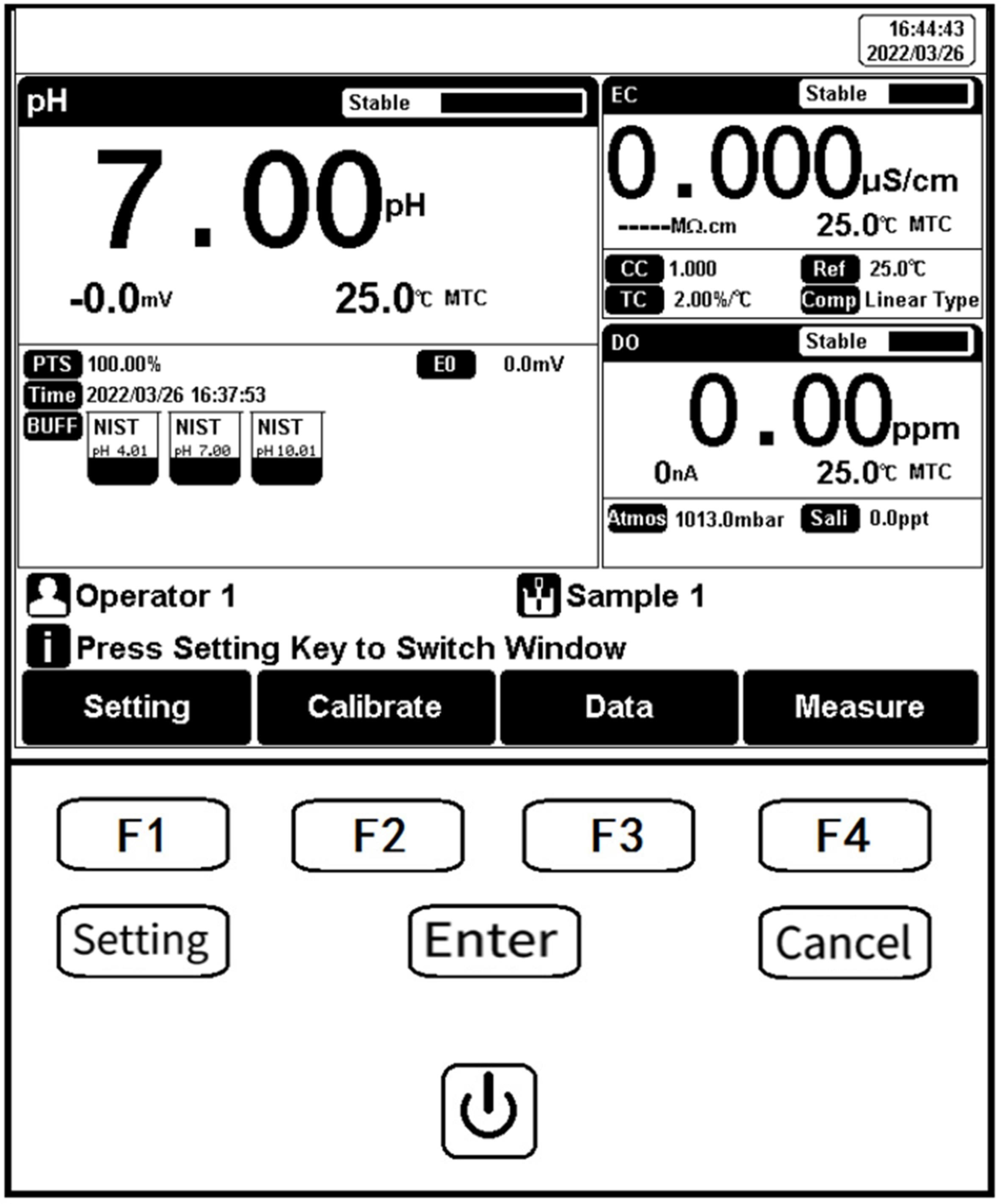
Figure 6
Function keys explanation
Key Function Explanation
| No. | Key | Explanation | Note |
| 1 |  | Power | Press to switch on/off |
| 2 |  | Setting | Set the parameters and settings |
| 3 |  | Cancel | Cancel the operation |
| 4 |  | Enter | Confirm the option |
| 5 |  | F1 | Function key, Corresponds to the function options on the screen |
| 6 |  | F2 | Function key, Corresponds to the function options on the screen |
| 7 |  | F3 | Function key, Corresponds to the function options on the screen |
| 8 |  | F4 | Soft function keys, corresponding to the functions on the screen |
Table 10
5.4 Parameter Settings
In the measuring, users can set the instrument parameters by pressing "Setting" to set the measuring parameters.5.4.1 Tutorial settings
For the first use, please follow the guide to settings the measurement parameters. After all the settings, press the "Enter" to return to the previous page.5.4.2 Select parameters
The instrument contains up to 3 measurement modules, and each measurement function can select different measurement parameters (Switch the parameters by clicking on the blank area of measurement box on screen). The detail is shown in the following table:Instrument Measurement Parameters
| Modules | Measurement parameters |
| pH/pX measurement function | pH, mV, ORP, pX, ion concentration |
| Conductivity measurement function | Resistivity, conductivity, TDS, salinity, ash |
| Dissolved oxygen measurement function | Dissolved oxygen current, dissolved oxygen concentration, saturation |
| Temperature measurement function | Temperature |
Table 11
Select the proper measurement parameters to perform a measurement. The screen displays the detail of three measurement parameters when three modules are chosen. Two parameters are shown as two modules are chosen. A single parameter is shown by one measurement method being selected.
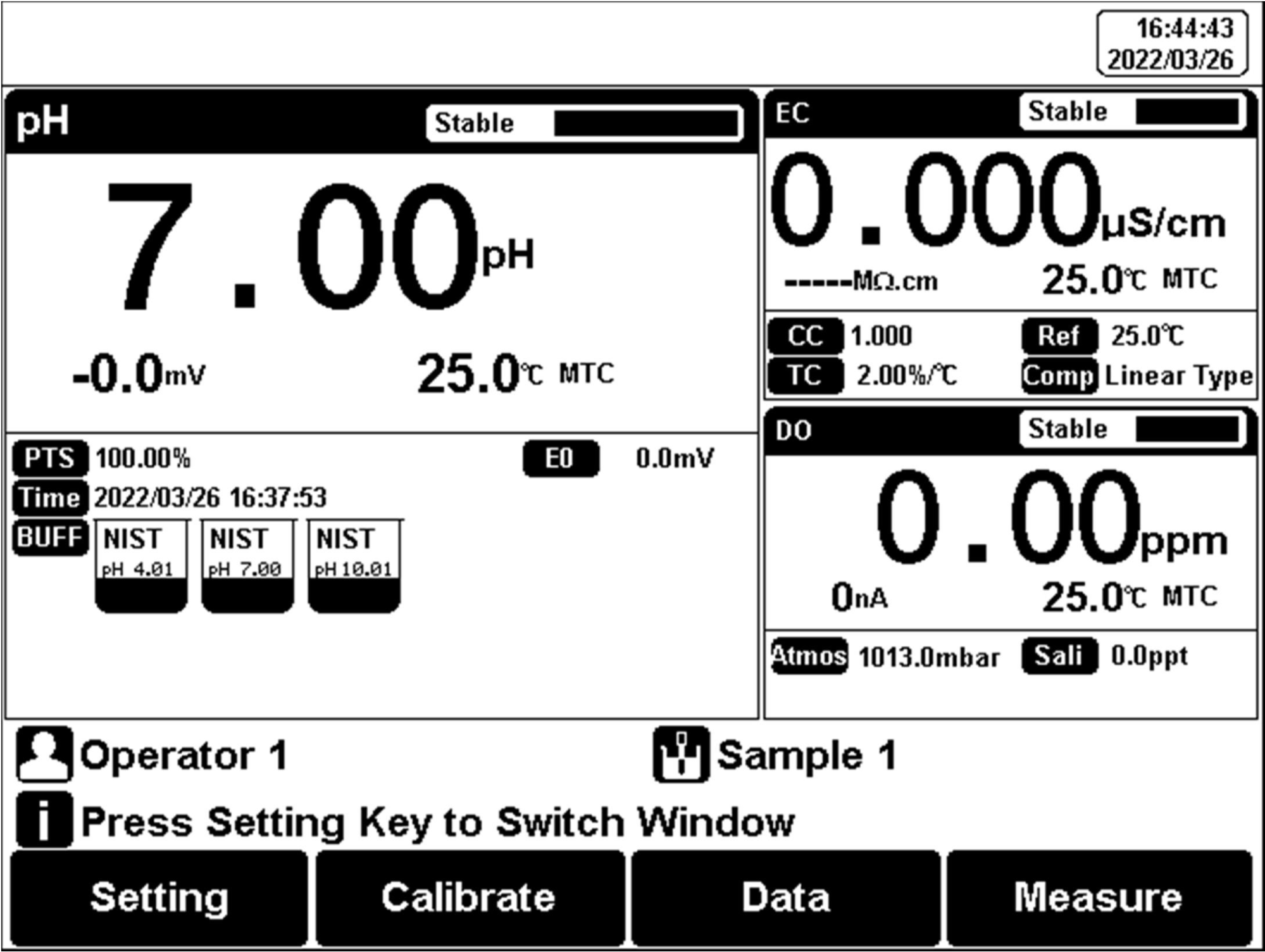
Figure 7
Three-parameter measurement
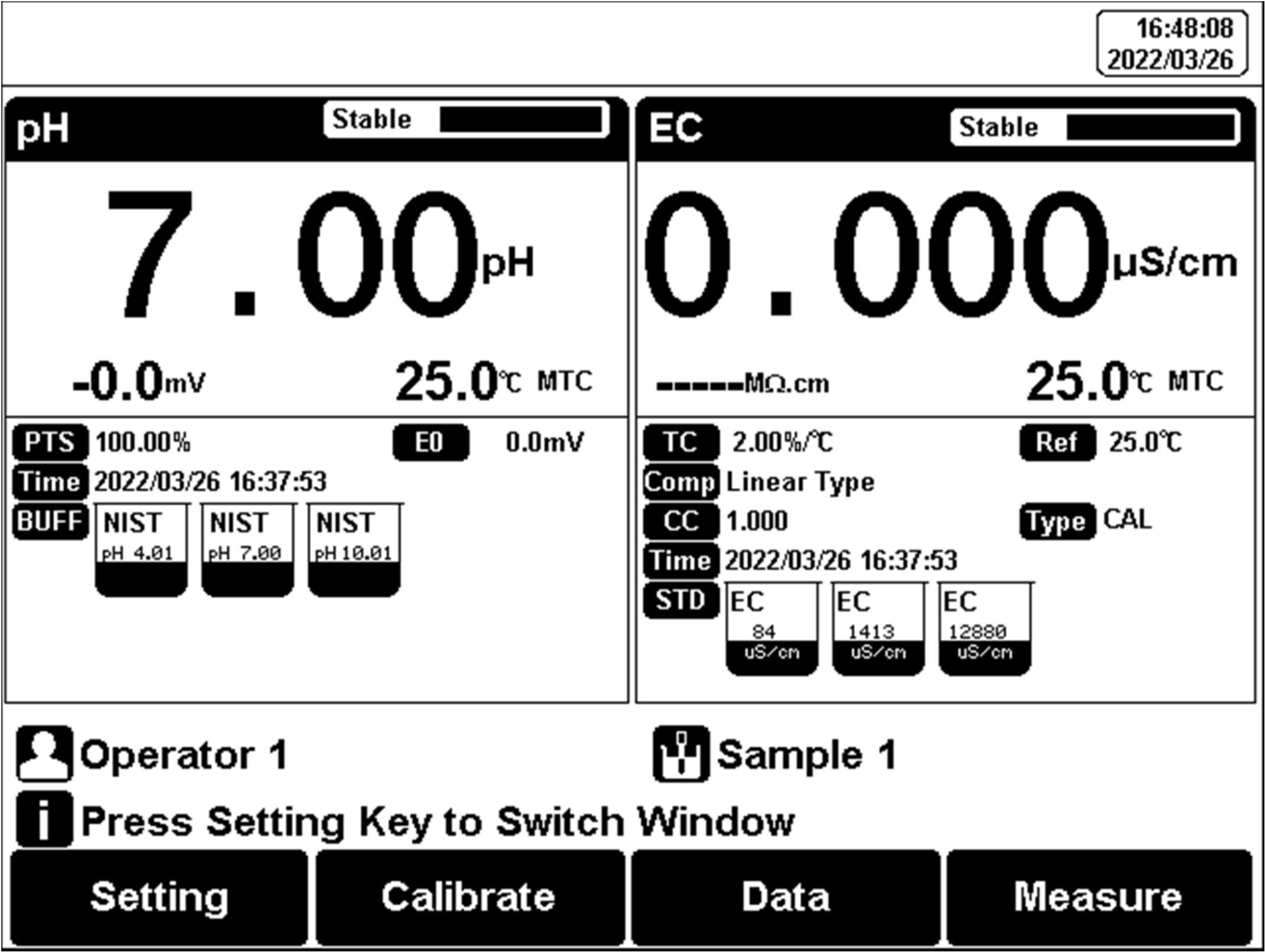
Figure 8
Two-parameter measurement
5.4.3 Reading Mode Settings
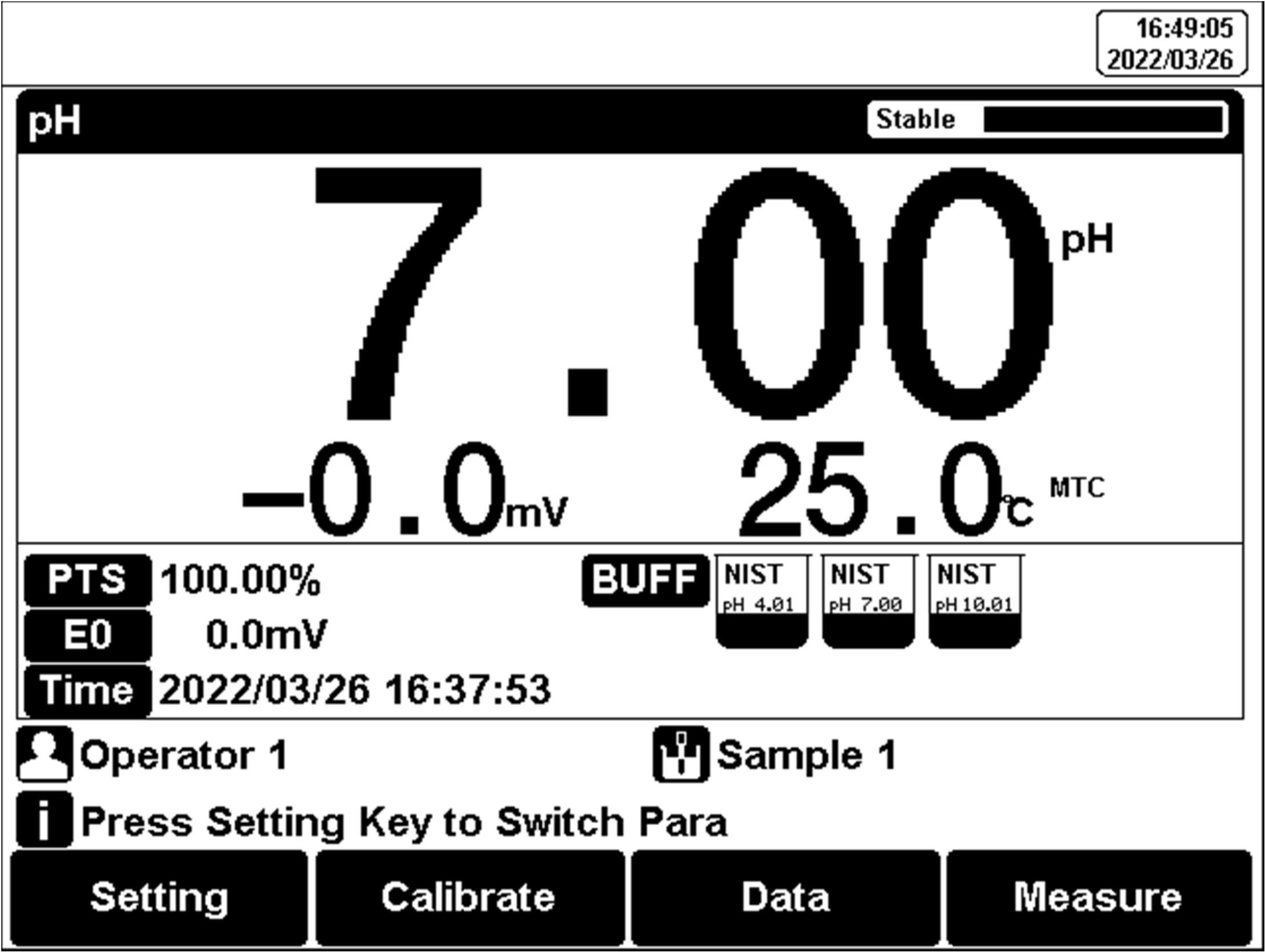
Figure 9
Single-parameter measurement
The meter provides three reading modes, including continuous reading, auto reading, and timed reading.
Continuous reading: The instrument displays real-time measurement results. Users can end the measurement at any time and save the last result. Auto-reading: The measurement reached the balance, and the meter locked the reading result. The meter offers "Fast", "Medium", "Strict" and "Custom" four options for endpoint detection conditions. Time reading method: Timed Reading contains two kinds of timed reading methods: "Interval Measurement" and "Timed Measurement". "Interval Measurement" provide measurement results at interval time and "Timed Measurement" provide measurement result after a set time.
Reading Parameters Settings
| Stability Type | pH | ISE/pX | Conductivity | DO | |
| Fast | Stable time | 4s | 4s | 5s | 5s |
| Fluctuation | 1mV | 0.6mV | 1.0% | 4nA | |
| Medium | Stable time | 6s | 8s | 8s | 8s |
| Fluctuation | 0.5mV | 0. 2mV | 0.4% | 3nA | |
| Strict | Stable time | 8s | 12s | 15s | 15s |
| Fluctuation | 0.1mV | 0.1mV | 0.1% | 2nA | |
| Custom (Recommended value) | Stable time | 1 to 30s | 1 to 30s | 1 to 30s | 1 to 30s |
| Fluctuation | 0.1~1mV | 0.1~1mV | 0.1~2% | 2 to 5nA | |
Table 12
5.4.4 pH Parameter Settings
5.4.4.1 pH standard groupsThe meter provides various Standards Group including DIN, NIST, GB, and USA. And allows the user to prepare the customized Standard groups.
Standard Solution Groups
| Groups | Contents |
| GB | 1.68pH, 3.56pH, 4.00pH, 6.86pH, 7.41pH, 9.18pH, 12.46pH |
| DIN | 1.68pH, 2.00pH, 3.56pH, 3.78pH, 4.01pH, 6.87pH, 7.00pH, 7.42pH, 9.18pH, 10.01pH, 12.45pH |
| NIST | 1.68pH, 4.01pH, 6.86pH, 7.00pH, 7.42pH, 10.01pH, 12.47pH |
| USA | 1.680pH, 4.010pH, 7.000pH, 10.010pH |
Table 13
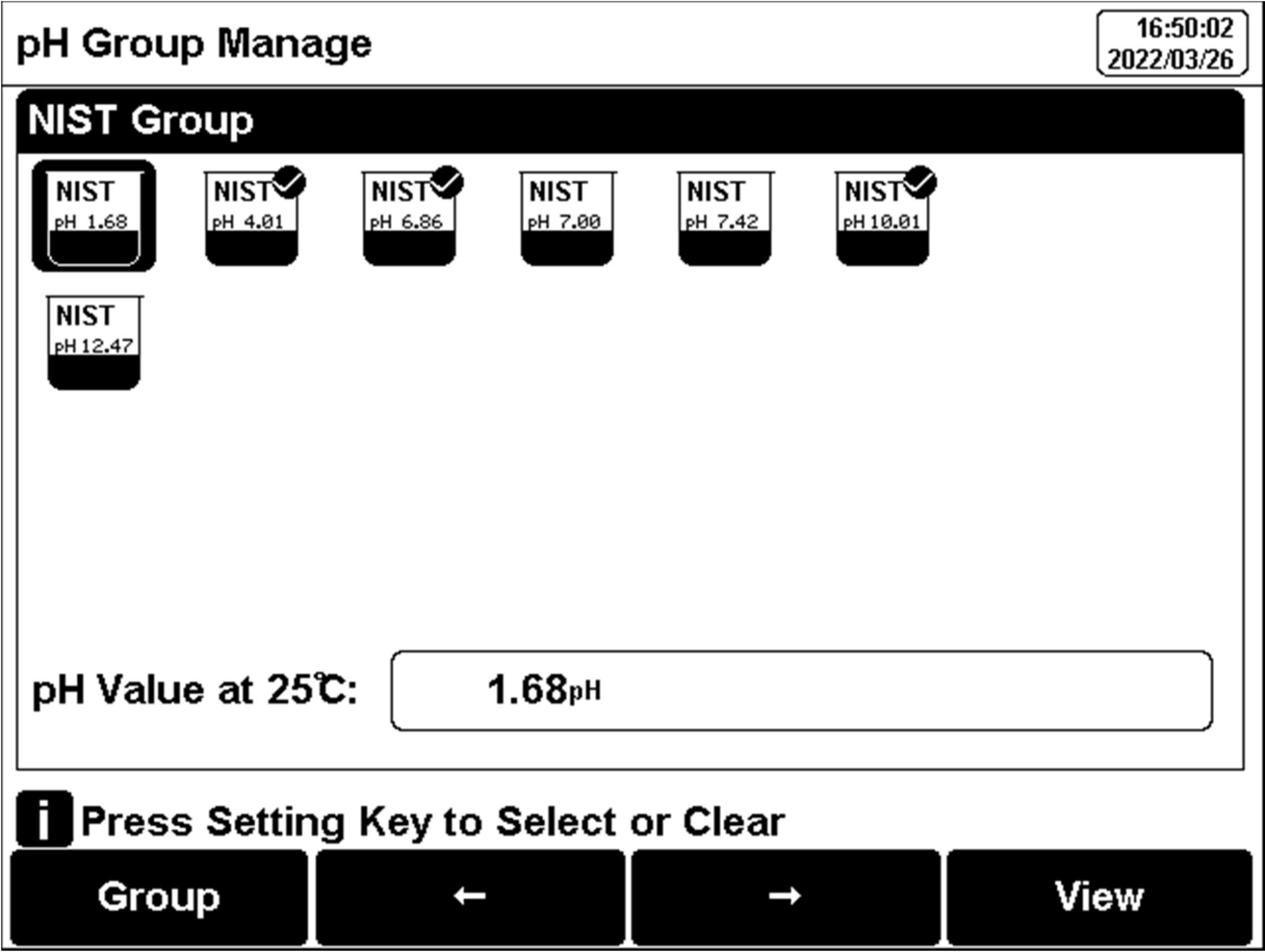
Figure 10
Selection of standard groups and standard solution
The meter supports up to five-points calibrations. Neighboring standards (pH gap<2) choice in the group may be frozen for accurate calibration. For neighboring standards, please choose the customization to perform calibration.
 【TIPS】
【TIPS】If the selected standard solution group is different from the pH standard buffer solution used, it will lead to wrong calibration results.
5.4.4.2 Recognition
Auto Mode and Manual Mode.
In some special cases, it is necessary to use some non-standard pH buffer solutions, or use two very close pH standard buffer solutions for electrode calibration. In this case, the manual standard solution identification function can be used. When set to "manual mode", the pH value of the current standard solution can be input during and used for electrode calibration.
5.4.4.3 Resolution settings
The pH measurement resolution of the instrument is adjustable. pH Resolution: 0.01pH and 0.1pH. mV resolution: 0.1 mV and 1 mV.
5.4.5 pX/ISE Parameter Settings
5.4.5.1 Ion mode selectionThe ISE measurement methods provide by meter include Ag+, Na+, K+, NH4+, Cl-, F-, NO3-, BF4-, CN-, Cu2+, Pb2+, Ca2+, etc., also support customized ions.
5.4.5.2 Resolution settings
The PX/ISE measurement resolution of the instrument is adjustable. pX resolution: 0.01pX and 0.1pX.mV resolution: 0.1 mV and 1 mV.
5.4.6 Conductivity Parameter Settings
5.4.6.1 EC calibration typeEC calibration type: Cal by Standards and input manually.
CAl By Standards: Cell constant is calibrated with standard conductivity standard solution.
Input manually: It allows the user to set the cell constant.
5.4.6.2 Manual standard recognition
For neighboring standards, please choose the customization to perform calibration.
5.4.6.3 Conductivity electrode type
Conductivity electrode: Four conductivity cell constant 0.01, 0.1, 1, 10. The defaulted conductivity cell constant is 1. Users need to enter the cell constant value on the label of the conductivity electrode for accurate measurement.
The electrode constant corresponds to the measurement range of conductivity, resistivity and TDS
| No. | Cell Constant | Range |
| Conductivity Range | 0.01cm -1 | (0.000~19.99)μS/cm |
| 0.1cm -1 | (0.200~199.9)μS/cm | |
| 1.0cm -1 (platinum black) | 2.000μS/cm~199.9mS/cm | |
| 10cm -1 | 20.00μS/cm~1000mS/cm |
| Resistivity Range | 0.01cm -1 | 20.0MΩ·cm~50.0kΩ·cm |
| 0.1cm -1 | 2.00MΩ·cm~5.00kΩ·cm | |
| 1.0cm -1 (platinum black) | 200.0kΩ·cm~5.00Ω·cm | |
| TDS Range | 0.01cm -1 | (0.000~9.99)ppm |
| 0.1cm -1 | (0.100~99.9)ppm | |
| 1.0cm -1 (platinum black) | 1.000 ppm~99.9 ppt | |
| 10cm -1 | 10.00 ppm~300 ppt |
Table 14
5.4.6.4 EC Reference temperature
Conductivity reference temperature: The conductivity of the solution is greatly affected by temperature, to make the conductivity measurement results at different temperatures comparable, the conductivity and temperature values at the time of measurement are usually recorded and converted into the conductivity value at a certain temperature through temperature compensation, which is the reference temperature. The instrument allows settings of 20.0°C,25.0 °C 2 reference temperatures, the default reference temperature is 25 °C.
5.4.6.5 EC Compensation
EC Compensation Mode: Three different compensation modes can be used for various applications. The meter supports Linear type, DI water type, and non-comp type.
1) Linear type: Linear compensation is usually used for the measurement of medium and high conductivity solutions. With linear compensation, you can set the temperature compensation coefficient, which defaults to 2.00%/°C (approximately the temperature compensation coefficient of a sodium chloride solution at 25°C). It allows the user to set the temperature coefficient.
2) DI water type: DI water compensation is usually used for the measurement of pure water and ultrapure hydropower conductivity below 5μS/cm. It allows the user to set the temperature coefficient.
3) Non-comp type: Non-compensation is usually used to obtain the true conductivity value at the measured temperature.
5.4.7 Dissolved Oxygen Parameter Settings
5.4.7.1 DO salinity compensation settingsSalinity is the amount of sodium chloride dissolved in 1 L of water, in g/L. The dissolved oxygen concentration of water is highly affected by salinity. Typically, for every 1 g/L increase in salinity, the saturated dissolved oxygen of water decreases by 0.0559 mg/L or ppm.
Users can set salinity compensation on the setting page. The salinity compensation range of measurement is (0.0~50.0) g/L.
 【TIPS】
【TIPS】If the sample has high salinity, salinity compensation is required to obtain accurate results.
5.4.7.2 Atmos compensation
Atmospheric pressure is an important factor for dissolved oxygen concentration and dissolved oxygen saturation measurement. The meter supports automatic barometric compensation and manual barometric compensation modes in the range of (600~1100) mbar. The default atmospheric pressure is 1013.0mbar in manual compensation mode.
Users can select the necessary compensation mode and pressure unit for measurement in the setting.
 【TIPS】
【TIPS】Atmos compensation is important for measurement results in low atmospheric pressure areas.
5.4.8 Temperature Parameter Settings
The temperature unit of the meter is selectable in °C and °F. Temperature compensation mode: ATC and MTC.ATC means automatic compensation. It allows the user to select the 4 pins socket or 5 pins socket.
MTC means manual compensation. It allows the user to input the temperature.
 【TIPS】
【TIPS】ATC input selection. For single-parameter measurement, please follow the above instruction. When conductivity compensation electrode dissolved oxygen electrode is applied, the default ATC input is from DO electrode. If the ATC input selection is incorrect, try resetting or manually entering the temperature.
5.4.9 Data Management Settings
5.4.9.1 Sample ID typeThe instrument supports three setting methods of Sample ID: number order, time order, and manual.
Number order: The sample ID No. is increasing with series number. Time order: The sample ID No. is increasing with sample measuring time. Format: Year/Y, Month/M, Day/D, Hour/H, Minutes/M, Second/S Manual: Manually set the sample ID No. It allows samples to manually enter the sample ID when saving or printing data.
5.4.9.2 Result Autosave
When this function is enabled, the meter saves the results when the reading is stable in the auto-reading and interval timed reading mode.
5.4.9.3 Data Overwrite
The meter provides 500 sets of measurement results storage space. When this function is enabled, the results data that exceeds capacity will overwrite the old results data.
5.4.10 Output option
The data format is GLP, STD Format, and Custom. It could select one data format to output the result.5.4.11 The user ID Settings
Set the user ID.5.4.12 System Parameter Settings
5.4.12.1 System Date & TimeSettings of system date and time.
5.4.12.2 Buzzer setting
Users can set the key sound by this setting.
5.4.12.3 Brightness setting
Users can adjust the screen brightness by this setting.
5.4.12.4 Auto Power off
The meter provides an auto shutdown function. When the meter is not used, the meter switches off automatically.
5.4.12.5 Restore Default
The meter supports "Restore Default" and "Restore Parameters". "Restoring Default" will restore all meter parameters to the factory state. "Restoring parameters" will restore the measurement parameters to the factory state.
5.4.12.6 Software version
Users can find the software version information on the general setting page.
5.5 pH Measurement
5.5.1 Calibration Preparation
The electrode slope and zero potential of pH electrodes drift slightly over time. To accurately measure pH, it is recommended to calibrate the pH electrode before use, the instrument supports 1-5 points calibration.One point calibration is a calibration process with a single standard solution, commonly applied in a quick test. The calibration slope is 100% here.
Two-point calibration is to use two pH standard buffer solutions to calibrate the electrode and construct a linear calibration curve through two points. Two-point calibration is the most commonly used calibration method, and it is usually recommended that the pH value of the solution be measured lies between the two standard buffer solutions. Two-point calibration can improve pH measurement accuracy.
Multi-point calibration is a calibration process with more than one standard solution. It is recommended to calibrate between two standard buffer solutions at the pH of the solution to be tested. Multi-point calibration covers a wider measurement range for accurate pH measurement. Before starting calibration, please prepare one or more pH standard buffer solutions.
5.5.2 Standards group selection
Before starting calibration, please prepare one or more pH standard buffer solutions. The meter has a standards recognition function. Please set the Standard Group before the measurement.You can also set the identification type to "Manual Mode" and manually enter the nominal value during the calibration process.
5.5.3 pH Calibration
The calibration process is as follows:1. Setting.
1) Set the parameters (e.g., pH).
2) Select NIST standard solution group, and check pH 4.01, pH 7.00, and pH 10.01 three standard solutions.
3) Set the Auto Mode recognition.
2. Connect the ATC probe or enter the temperature manually.
3. Press the F2 "Calibrate" for one-parameter measurements or press the F2 "Calibrate"- "pH Calibration" for multi-parameter measurements.
4. Put the cleaned electrode into a pH 4.01 standard solution.
5. Wait for the instrument to display “Auto Mode Matched”, and press the F4 “Start”.
6. If only 1-point calibration is required, after 1-point calibration is completed, press the "Enter" key to complete the calibration.
7. If multi-point calibration is required, please replace the pH7.01 and pH10.01 standard buffer solutions. After cleaning the electrode, place the electrode into the standard solution. After the instrument recognizes it successfully, the instrument reads stably, press the F4 "Next Point" to complete the calibration.
8. After completing the calibration, press the "Enter" key to complete the calibration, save the calibration results and end the calibration, and directly enter the start interface. If the checked standard solution group is 5, automatically end the calibration after five points of calibration.
5.5.4 pH Measurement
After the calibration, press "Measure" to start a measurement.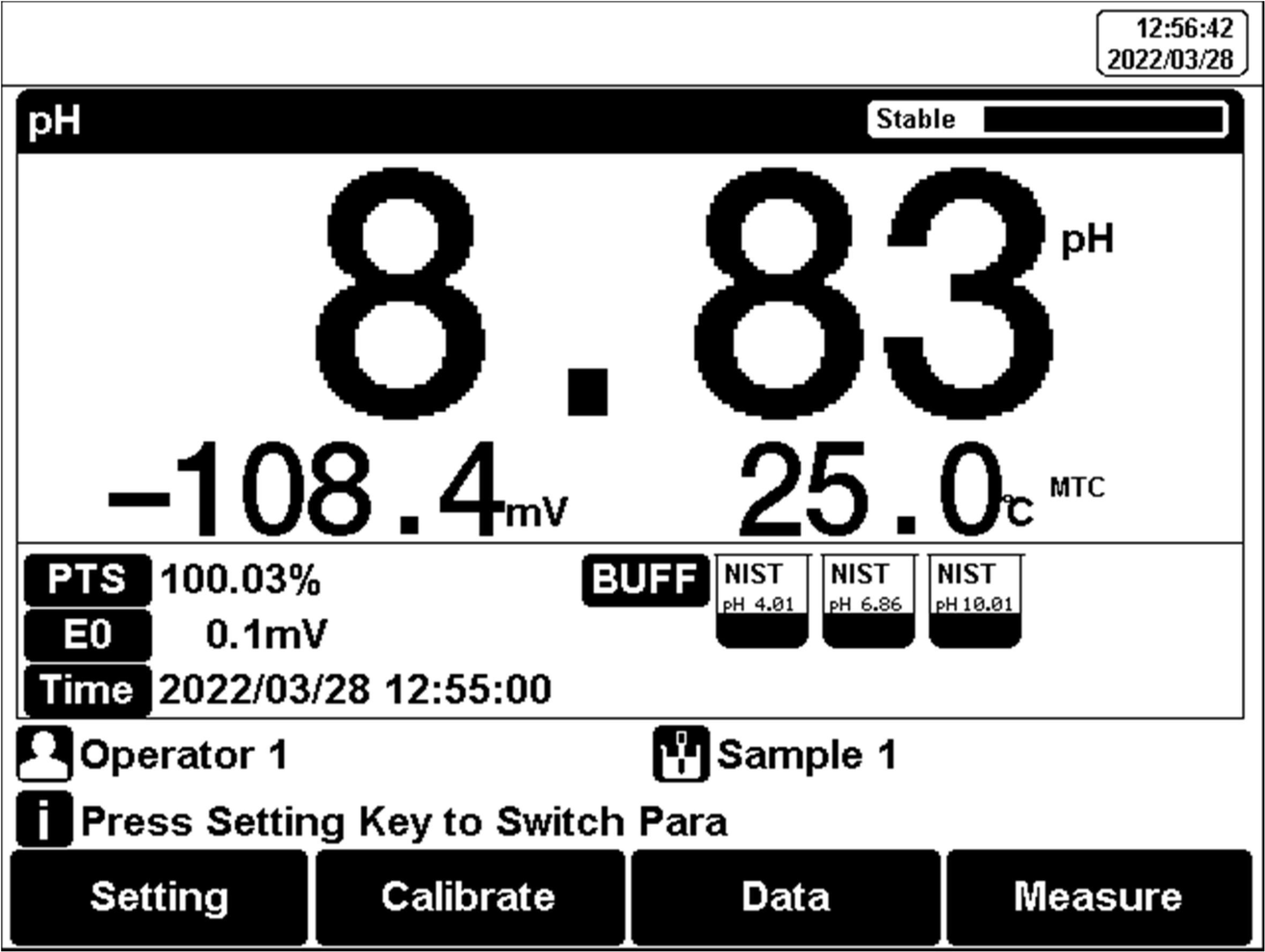
Figure 11
pH measurement information
The measurement process is as follows:
1. Setting.
1) Set the parameters (e.g., pH).
2) Set the reading mode (e.g., continuous reading, auto-reading, or timed format).
2. Put the electrode into the test solution under test.
3. In the idle status, press F4 "Measure" to enter into measurement status.
4. When the reading is stable, press "Enter" to read the results.
5. Press the "Save" to save the measurement results.
6. Press the "Output" to print the measurement result when connect to the printer.
7. Between measurements, stored pH electrode in distilled or deionized water.
8. After measurement, rinse the pH electrode with deionized water thoroughly.
 【TIPS】
【TIPS】The measurement end of the electrode should well be immersed into the sample solution. For high accuracy measurement, make sure the measurement is carried out at the lab with constant temperature and pressure. If the two temperatures are different, it is recommended to use a pH combination electrode with temperature compensation or use a separate temperature electrode for automatic temperature compensation. Or use a thermometer to measure the temperature of the current solution and manually set the temperature for manual compensation.
5.6. Ion Measurement
5.6.1. Calibration Preparation
The accuracy of the electrode slightly decreases over time. For an accurate measurement, electrode calibration is necessary. See the electrode instructions for specification.5.6.1.1 Ion-selective electrodes
The ion-selective electrode is based on the ion-selective membrane, which can be divided into a single crystal membrane, salt membrane, glass membrane, and PVC ion-selective membrane. Ion-selective electrodes usually have single electrodes and composite electrodes, composite electrodes are more convenient and simpler in the operation. The meter requires a composite electrode.
5.6.1.2 Ionic strength adjustment buffer
The use of ion electrodes to measure ion concentration requires the addition of an ionic strength adjustment buffer.
The ionic strength of a solution has an important influence on the measurement of ion concentration. On the one hand, the ion-selective electrode directly measures the activity of the ion, α = γc. Wherein, α is the activity of the ion, γ is the activity coefficient of the ion, and c is the ion concentration. Usually, the activity coefficient γ is affected by the ionic strength in the solution. By adding an ionic strength adjustment buffer to the standard solution and the test solution, the measured solution has a similar ionic strength to the standard solution, thereby having a similar activity coefficient γ. On the other hand, if a solution with low ionic strength, the potential of the reference electrode will show instability. The addition of the ionic strength adjustment buffer can help stabilize the reference electrode.
Various ion measurement needs various ionic strength adjustment buffer. Common ionic strength adjustment buffers are recommended in the following table.
Recommended ionic strength adjustment buffer
| Ions’ category | ionic strength adjustment buffer |
| Na + | 0.2 mol/L diisopropylamine |
| F - | 0.1 mol/L NaCl or TISAB |
| Cl - | 0.1 mol/L KNO 3 |
| Br - | 0.1 mol/L KNO 3 |
| I - | 0.1 mol/L KNO 3 |
| Ag + | 0.1 mol/L NaNO 3 |
| Cu 2+ | 0.1 mol/L NaNO 3 |
| Pb 2+ | 0.1 mol/L KNO 3 |
| S 2- | 0.1 mol/L KNO 3 |
| K + | 0.05 mol/L MgAc 2 |
| Ca 2+ | 0.1 mol/L KCl |
| NO 3 - | 0.1 mol/L NaH 2 PO 4 |
| BF 4 - | 0.1 mol/L Na 2 SO 4 |
| ClO 4 - | 0.1 mol/L NaCl |
Table 15
5.6.1.3 Preparation
Please prepare standards according to ISO guidelines or buy locally.
5.6.1.4 Activation of the ISE electrodes
When the electrode is used for the first time or has not been used for a long time, an activation is recommended. The electrode has better measurement performance after activation.
Ion electrode activation solution and activation time recommendation
| Ion category | Activation solution | Activation time |
| Na + | 10 -3 mol/L NaCl | 2h |
| F - | 10 -3 mol/L NaF | 2h |
| Cl - | 10 -3 mol/L KCl | 2h |
| Br - | 10 -3 mol/L NaBr | 2h |
| I - | 10 -3 mol/L NaI | 2h |
| Ag + | 10 -3 mol/L AgNO 3 | 2h |
| Cu 2+ | 10 -3 mol/L Cu (NO 3 ) 2 | 2h |
| Pb 2+ | 10 -3 mol/L Pb (NO 3 ) 2 | 2h |
| S 2- | 10 -3 mol/L AgNO 3 | 2h |
| K + | 10 -3 mol/L KCl | 2h |
| Ca 2+ | 10 -3 mol/L CaCl 2 | 2h |
| NO 3 - | 10 -3 mol/L NaNO 3 | 2h |
| BF 4 - | 10 -3 mol/L NaBF 4 | 2h |
| ClO 4 - | 10 -3 mol/L NaClO 4 | 2h |
Table 16
 【TIPS】
【TIPS】The activation time may variously be based on various activation solutions. See the ion-selective electrode manual for specifications.
5.6.1.5 Stirrer setting
The flow state of the solution influences the electrode potential of the ion-selective electrode. To improve the stability and repeatability of the measurement, it is recommended to use a stirrer to keep the flow rate of the solution stable during calibration and measurement.
5.6.2 Select Ion Type
The meter provides ion measurement methods of Ag+, Na+, K+, NH4+, Cl-, F-, NO3-, BF4-, CN-, Cu2+, Pb2+, Ca2+. Combination ISE electrodes are necessary.For an ion method not provided, a new method needs to be created. Press "Create", and fill in the information of ion to finish the ion method customization.
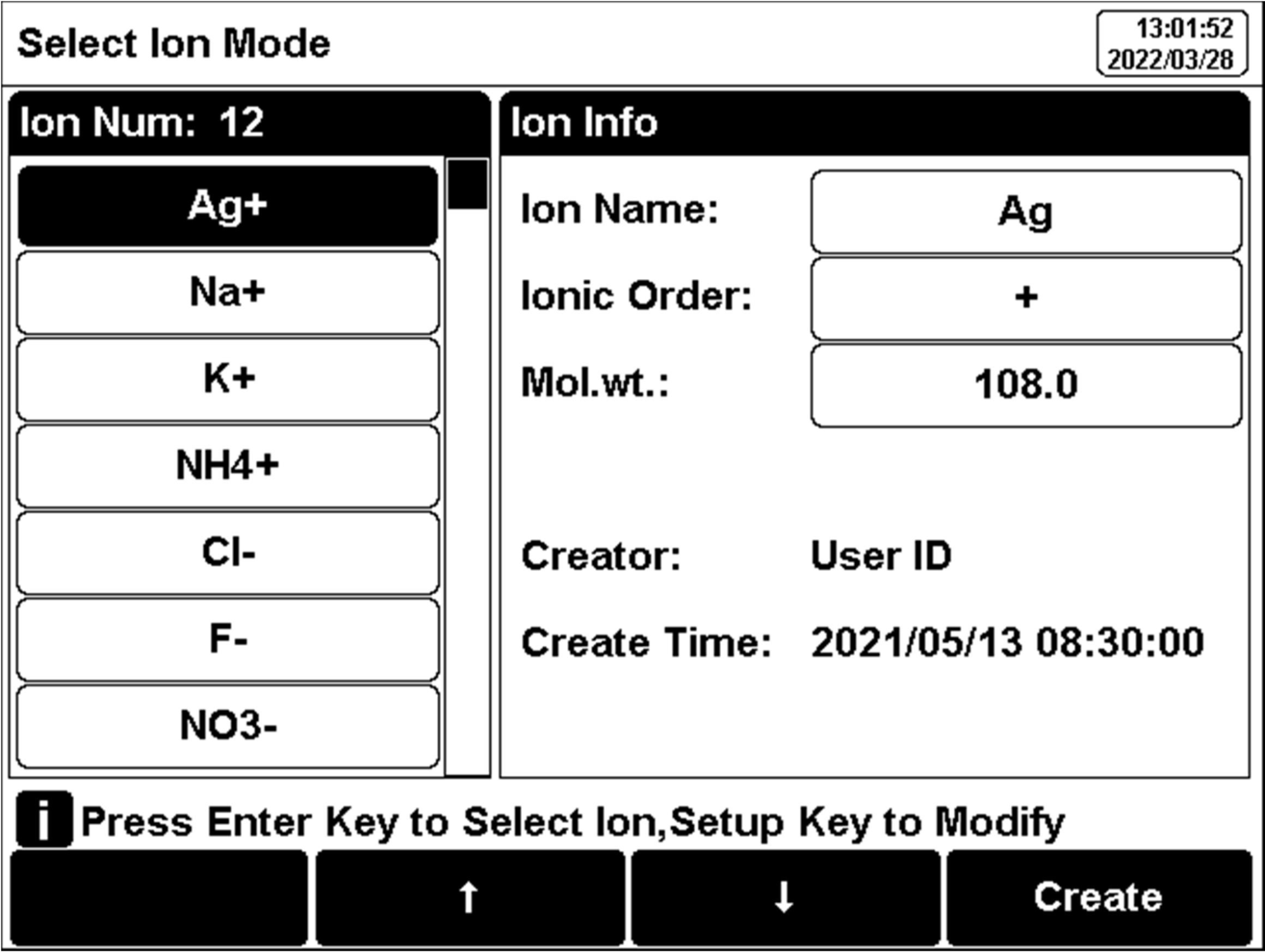
Figure 12
Ion mode selection
5.6.3 Measurement Mode Selection
Select the ion measurement methods by the user's needs. In general, when the direct-reading method is used for ion concentration measurement and pX measurement.Direct Reading Measurement is a commonly used ion concentration measuring method. The Direct Reading mode uses the following Nernst formula to calculate the concentration:
Ex E0 S log(Cx Cb )
Wherein,
Ex~ Equilibrium potential of the sample solution, in mV.
E0~ zero potential value, in mV.
S ~ Electrode slope (%).
Cx~ Concentration value of the sample solution, in mol/L.
Cb~ Blank concentration value in mol/L.
The electrode slope and zero potential value can be known from the calibration. When measuring the sample solution, the sample concentration result can be calculated from the formula. The direct-reading method is fast and suitable for quick test measurement of common samples.
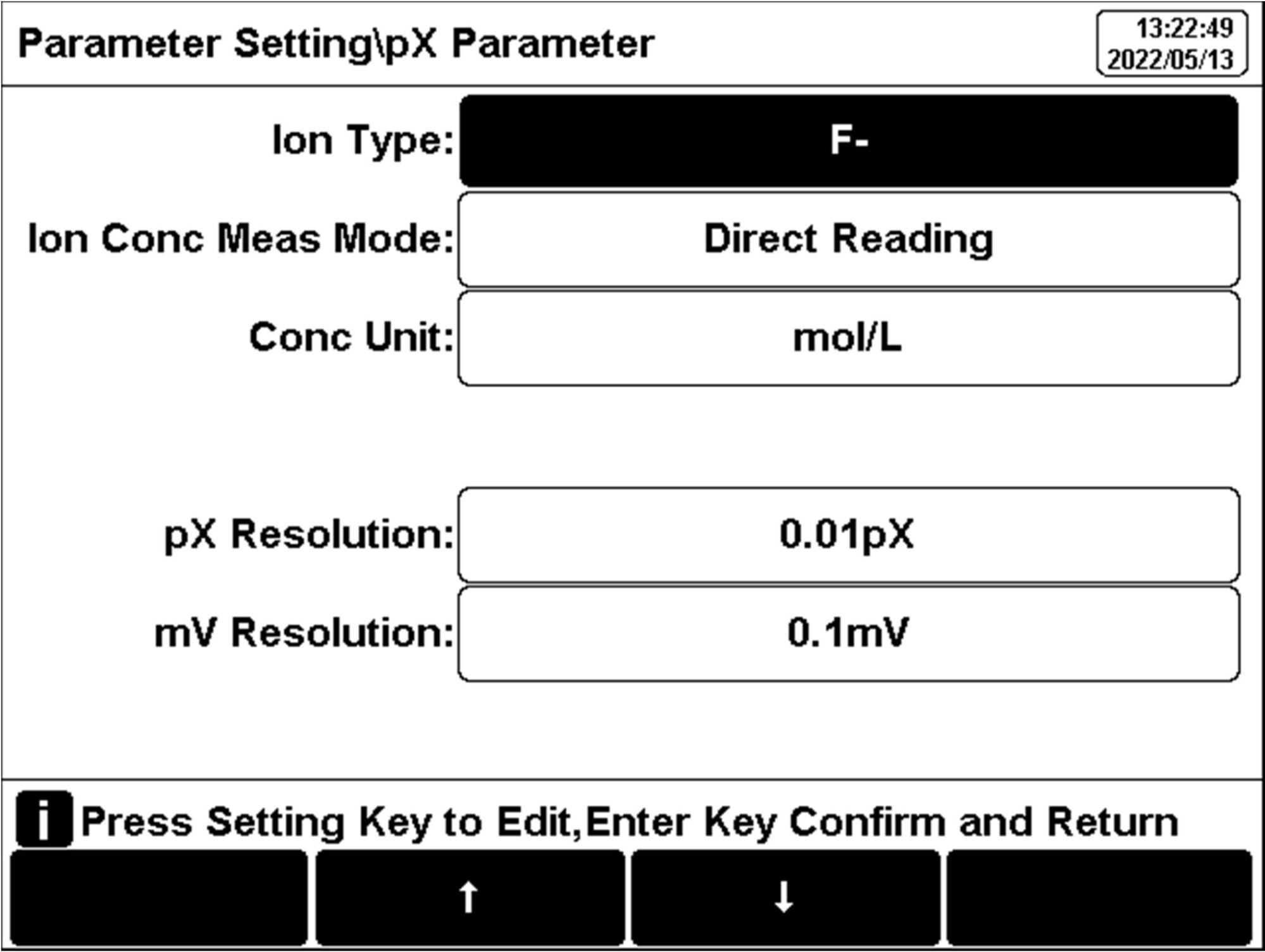
Figure 13
Direct reading method of pX/ISE measurement
The calibration setting process is as follows:
1) Press "pX para setup" to change the "Conc Meas Mode". Select "Direct Reading".
2) Set "Conc Unit", "Blank Conc", "Conc Resolution" and "mV Resolution".
5.6.4 pX/ISE Calibration
The pX/ISE calibration process is as follows:1. Add an appropriate amount of standard solution (usually 100 ml) to the beaker, then add an ionic strength adjustment buffer. Adjust the stirring speed of the solution for measurement.
2.Press the F2 "Calibrate"-"pX Calibration".
3.Put the cleaned electrode into a standard solution.
4.Press the F2 “STD value” to input the standard value of the standard solution.
5.Wait for the reading to be stable, and press the F4 “Start”.
6.If only 1-point calibration is required, after 1-point calibration is completed, press the "Measure" key to complete the calibration.
7. If choosing multi-point calibration (up to 5), press "Next Point" to repeat the operation.
8. If the checked standard solution group is 5, automatically end the calibration after five points of calibration.
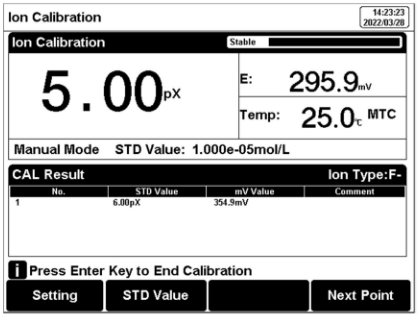
Figure 14
pX/ISE calibration information
 【TIPS】
【TIPS】➢ Please re-calibration for an unexpected measurement result.
➢ A room temperature test solution is recommended.
➢ It is recommended to calibrate from low concentration to high concentration standards.
5.6.5 pX/ISE Measurement
The measurement process is as follows:1.Setting
Set the parameters (e.g. pX) Set the ion type (e.g. F-) Set the direct reading as concentration means mode. Set the con concentration unit (e.g. ppm) Set the reading mode (e.g. continuous reading, auto-readind, or timed format).
2.Add an appropriate amount of standard solution (usually 100 ml) to the beaker, then add an ionic strength adjustment buffer. Adjust the stirring speed of the solution for measurement.
3.In the idle status, press F4"Measure" to enter into measurement status.
4.When the reading is stable, read the results.
5.Press the "Save" to save the measurement results.
6.Press the "Output" to print the measurement result when connect to the printer.
7. Between measurements, stored ISE electrode in distilled or deionized water.
8. After measurement, rinse the ISE electrode with deionized water thoroughly.
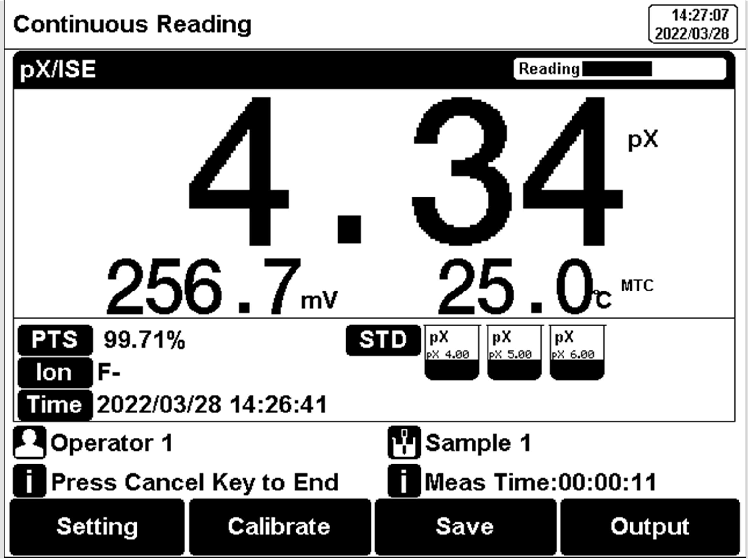
Figure 15
PX/ISE measurement information
After measuring a high ion concentration sample, the low concentration
ions measurement will be affected. In this situation, it is recommended to rinse the electrode as follows:
Add an appropriate amount of standard solution (usually 100 ml) to the beaker, then add an ionic strength adjustment buffer. Adjust the stirring speed of the solution for measurement. Rinse the ion-selective electrode with DI water, dry out and place it in a blank solution and place it in a blank solution to wait for the potential to stabilize. After taking out the electrodes, ready to perform the measurement.
 【TIPS】
【TIPS】Different ISE probes have different potential values in a blank solution. If the blank potential is away from the reference value, the user can do an activation to improve the performance of electrodes. If the electrode still does not meet the requirements, a new electrode is quite considerable.
 【TIPS】
【TIPS】Please re-calibration for an unexpected measurement result. A room temperature test solution is recommended. It is recommended to calibrate from low concentration to high concentration standards.
5.7 Conductivity Measurement
5.7.1 Cell Constant Input
Conductivity electrodes are precisely calibrated at the time of manufacture and marked with the exact cell constant. Before the measurement, by "Parameter Setting"- "EC Parameter" to enter the electrode cell constant.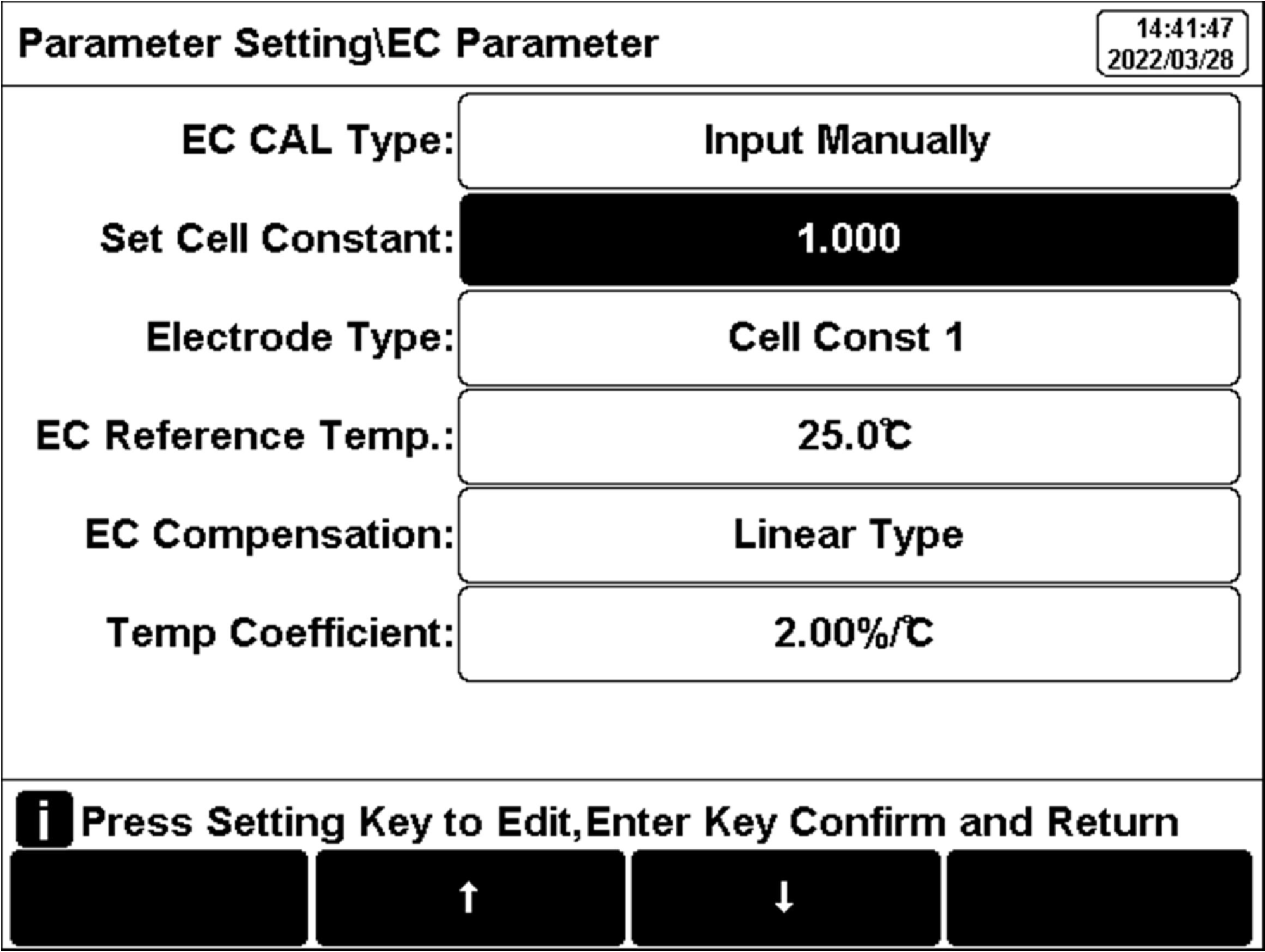
Figure 16
EC measurement information
5.7.2 Calibration Preparation
In general, conductivity electrodes need few calibrations. When the user gets an unexpected result, an electrode calibration is considerable.Usually, a single standard solution is required for calibration. For accurate measurement of sample conductivity above 50mS/cm, a two-point calibration is required. Two standards are required, a low conductivity standard and a conductivity standard close to the sample.
The meter provides various Standards Group including Universal
Standard Group and GB group. And allows the user to prepare the customized Standard groups.
5.7.3 Conductivity Calibration
After the measurement parameters are selected, press "Calibrate".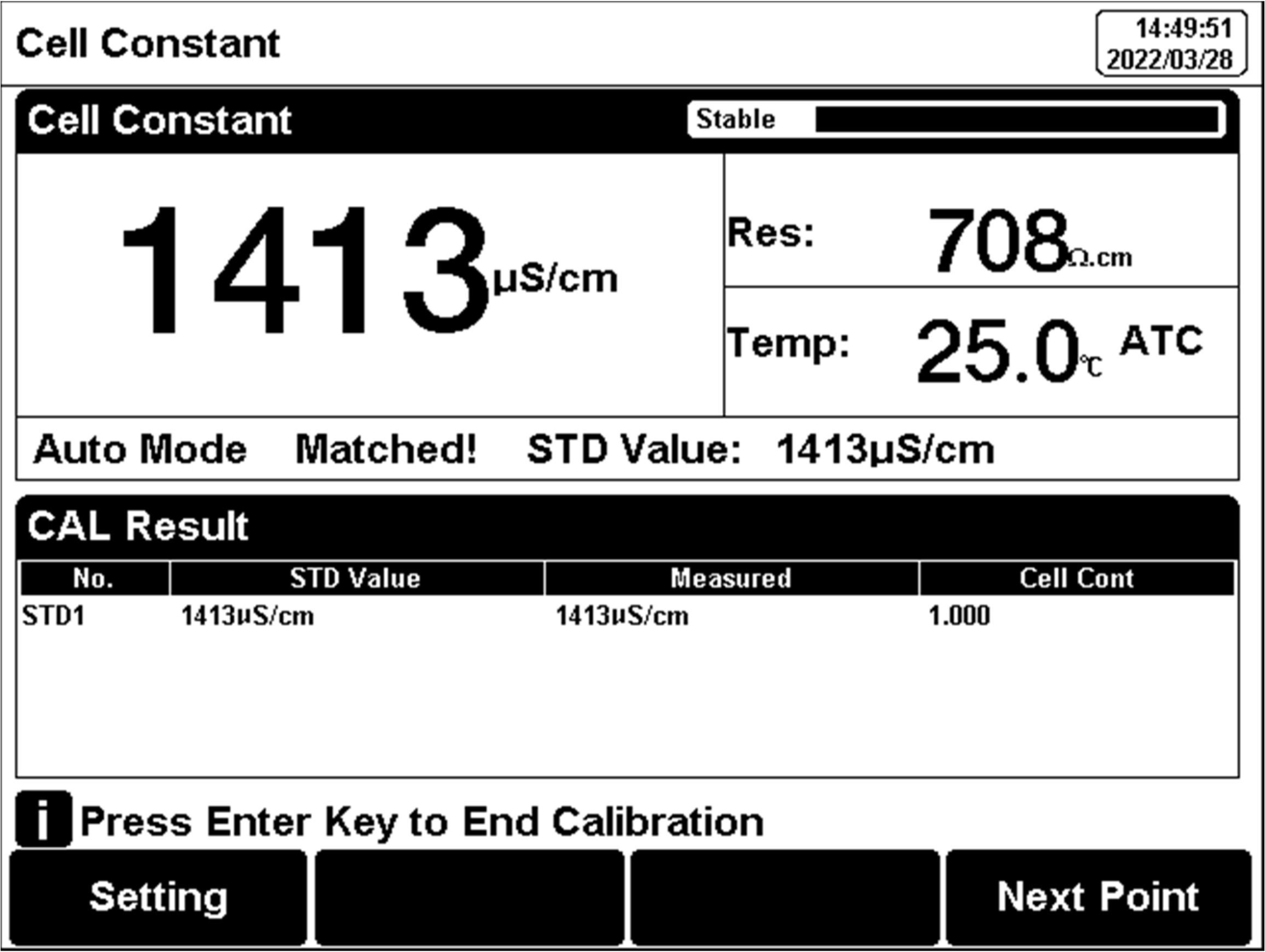
Figure 17
Electrode cell constant calibration information
For conductivity electrodes with different cell constants, it is recommended to use the following conductivity standard solutions for calibration.
KCl standards to electrode cell constants
| Cell constant (cm -1 ). | 0.1 | 1 | 10 |
| KCl solution Concentration (mol/L). | 0.001 | 0.01 or 0.1 | 0.1 or 1 |
Table 17
The calibration process is as follows:
1.In the idle status, press the soft button F1 "Setting" -"EC Parameter".
2.Press the "Constant type" to select the "1”.
3.Press "Cal. Type" to select the "Cal by Standards".
4.Prepare one or more standard conductivity solutions (e.g.,1413μS/cm conductivity solution).
5.Prepare a thermostatic bath, and set the temperature to (25.0±0.1) °C.
6.Place a standard conductivity solution in a thermostatic bath, and set the temperature to (25.0±0.1) °C.
7.Place the conductivity electrode into a standard solution.
8. When the conductivity and temperature reading (e.g.,1413µS/cm, 25.0℃) are stable, press the "Start".
9.If choosing one-point calibration, press "Enter" to end the calibration.
10.If choosing multi-point calibration (up to 3), press "Next Point" to repeat the operation.
11.The meter saves calibration data automatically and turns to idle status.
 【TIPS】
【TIPS】If the standard is not recognized, please check the connection of the probe and the contamination of standards.
 【TIPS】
【TIPS】The conductivity of the solution is greatly affected by temperature, it is recommended to use constant temperature water for calibration. Automatic or manual temperature compensation can also be optional when there is no water bath.
5.7.4 Conductivity Measurement
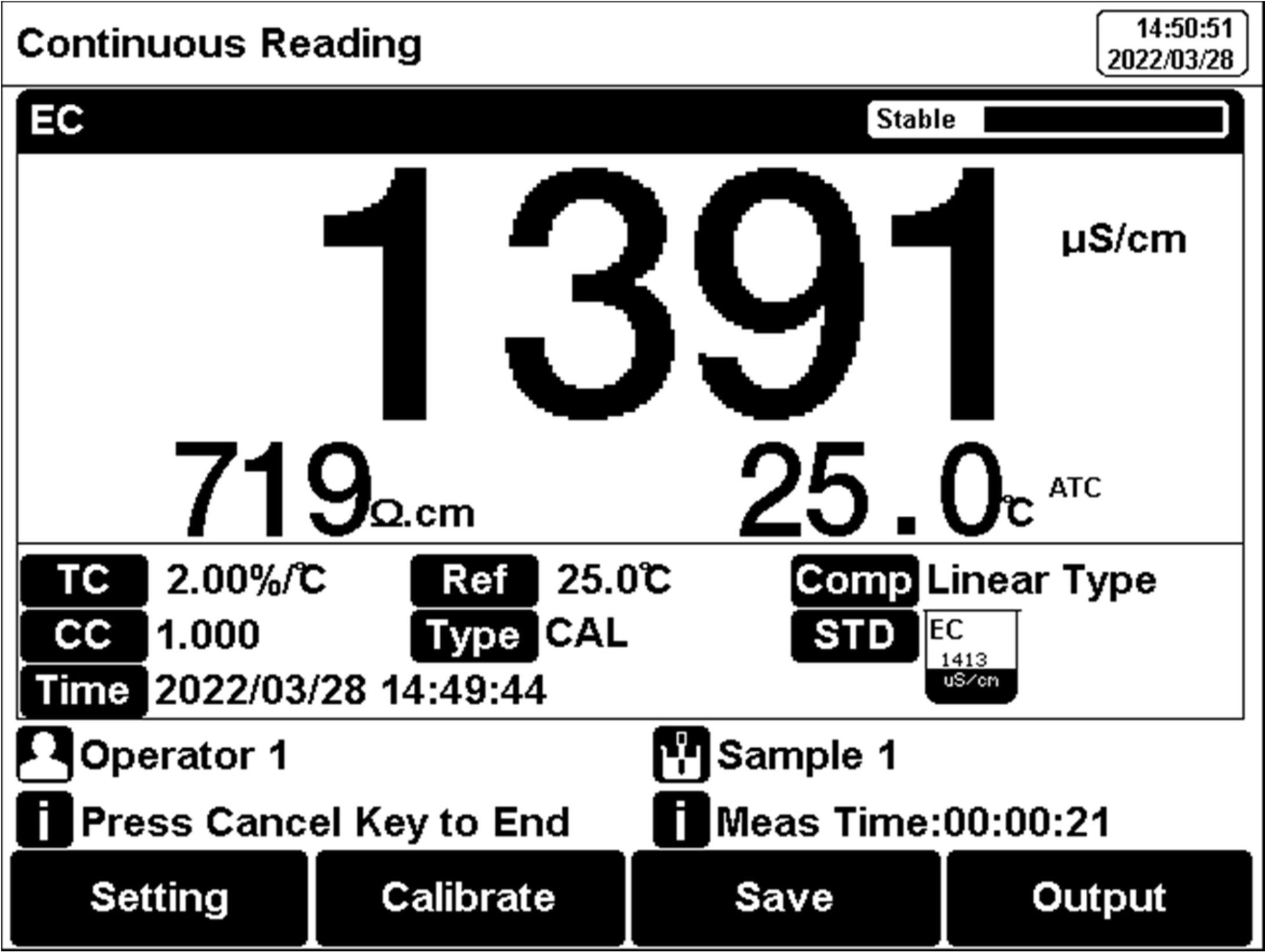
Figure 18
Conductivity measurement information
The measurement process is as follows:
1.Setting.
1)Set the parameters (e.g., conductivity). 2) Set the reading mode (e.g., continuous reading, auto-reading, or timed format). 3) Set the EC compensation (e.g., Linear compensation, temperature compensation coefficient 2.00%/°C). 4)Set the reference temperature (e.g., 25°C).
2.Rinse the conductivity electrode with DI water, and dry out.
3.Put the measurement end of the electrode into the sample solution.
4.In the idle status, press the soft button F4 "Measure" to enter into measurement status.
5.When the reading is stable, read the results.
6.Press the "Save" to save the measurement results.
7.Press the "Output" to print the measurement result when connect to the printer.
8.Between measurements, stored EC electrode in distilled or deionized water.
9.After measurement, rinse the EC electrode with deionized water thoroughly and put it on the electrode protection cap.
5.8 TDS Measurements
5.8.1 TDS conversion factor
5.8.1.1 Low Concentration TDS SampleFor samples with relatively simple composition and low concentration, the TDS of the solution can be estimated by conductivity. Compared with the weighing method, TDS estimation by conductivity is relatively simple and convenient with quite a good accuracy. The conversion factor between conductivity and TDS defaulting to 0.71, which can be used as the TDS coefficient for approximate estimation in most situations.
The conversion factor adjust process is as follows:
1.Press soft button F1 "Setting" -"TDS Parameter".
2.Select the TDSF CAL Type as the set TDS Factor.
3.Input the TDS factor as the desired TDS coefficient.
Conductivity to TDS Standard Solution
| Conductivity μS/cm | TDS standards | ||
| KCl(mg/L) | NaCl(mg/L) | 442(mg/L) | |
| 23 | 11.6 | 10.7 | 14.74 |
| 84 | 40.38 | 38.04 | 50.5 |
| 447 | 225.6 | 215.5 | 300 |
| 1413 | 744.7 | 702.1 | 1000 |
| 1500 | 757.1 | 737.1 | 1050 |
| 2070 | 1045 | 1041 | 1500 |
| 2764 | 1382 | 1414.8 | 2062.7 |
| 8974 | 5101 | 4487 | 7608 |
| 12880 | 7447 | 7230 | 11367 |
| 15000 | 8759 | 8532 | 13455 |
| 80000 | 52168 | 48384 | 79688 |
Table 18
442 indicated the solution contains 40%Na2SO4,40%NaHCO3,20%NaCl. The values listed in the table are values at 25°C.
5.8.1.2 High Concentrations TDS Sample Measurement
For samples with simple components and higher concentrations, such as high concentrations of NaCl solution, TDS factor re-calibration is needed.
For TDS measurements, the user may need to correct the TDS conversion factor by the TDS standard.
The conversion factor calibration process is as follows:
1.Setting.
Set the parameters (e.g., TDS). 2) Press soft button F1 "Setting" -"TDS Parameter". 3) Select the TDSF CAL Type as the set Cal by STD. 4) Set the reference temperature (e.g., 25°C).
2. Prepare TDS Standard.
3. Place a standard conductivity solution in a thermostatic bath, and set the temperature to (25.0±0.1) °C.
4.Rinse the conductivity electrode with DI water, and dry out.
5.Put the measurement end of the electrode into the sample solution.
6.Press the F2 "Calibrate"-"TDS Calibration".
7.Set the STD value as the sample STD value.
8.When the TDS and temperature readings (708ppm, 25.0℃) are stable.
9.If choosing one-point calibration, press "Enter" to end the calibration.
10. If choosing multi-point calibration (up to 3), press "Next Point" to repeat the operation.
11. The meter saves calibration data automatically.
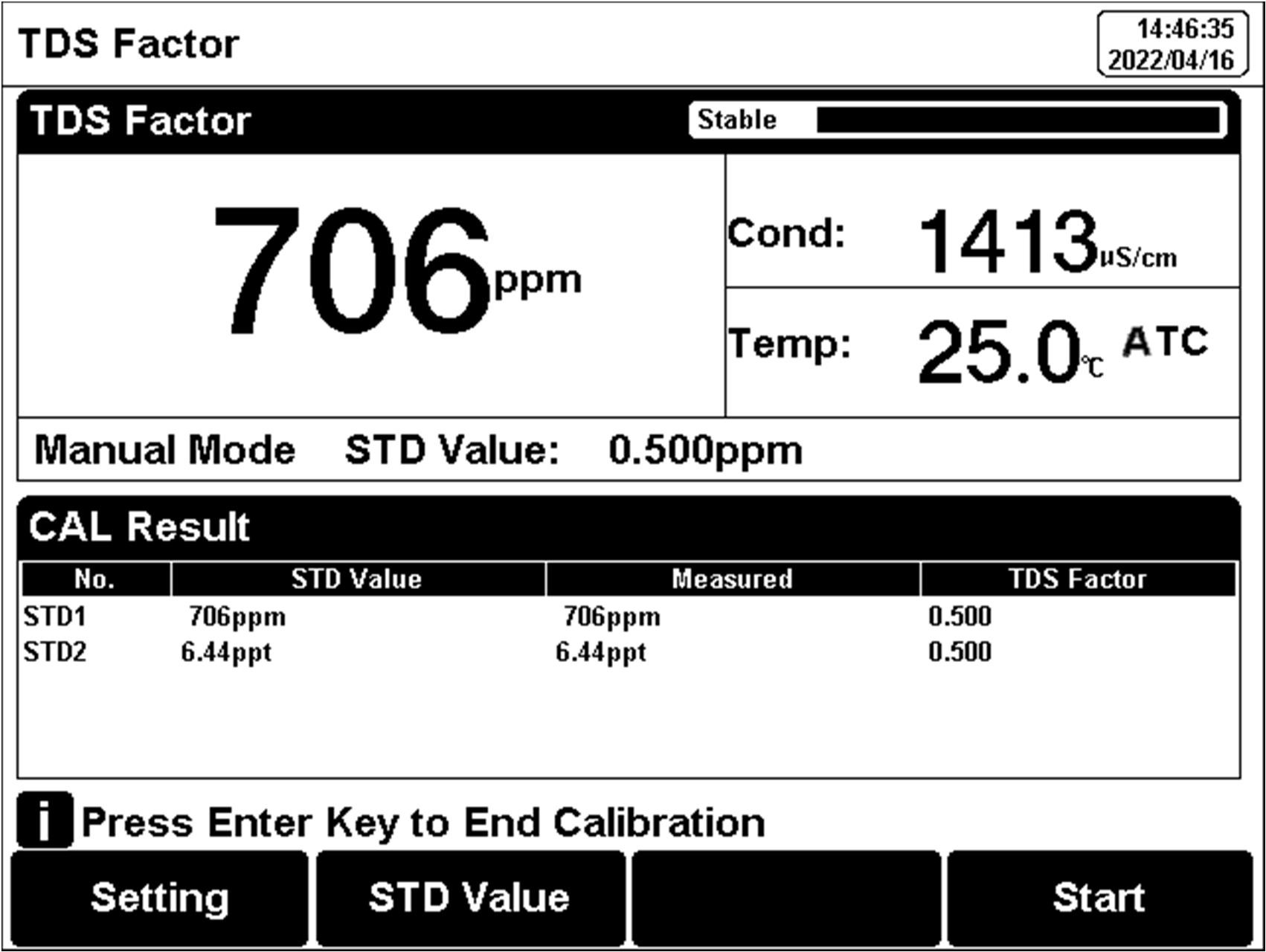
Figure 19
TDS coefficients calibration
5.8.1.3 Complex TDS Sample Measurement
For samples with complex compositions, the accuracy of TDS measurements can be improved by re-determination by laboratory methods and manual input of TDS coefficients. When the composition or concentration of the sample to be measured changes significantly, it is recommended to recalibrate the TDS coefficient.
The conversion factor calibration process is as follows:
1.Rinse the electrode with DI water. Put the measurement end of the electrode into the sample solution and set the temperature at (25.0±0.1) °C.
2.Using a weighing method to determine the TDS.
3.Calculate the TDS coefficient.
4.Press soft button F1 "Setting" -"TDS Parameter".
5.Select the TDSF CAL Type as the set TDS Factor.
6.Input the TDS factor as the desired TDS coefficient.
5.8.2 TDS Measurements
Users can switch the measurement parameter to TDS measurement by pressing the Conductivity/TDS measurement box on the screen.5.9. Salinity Measurement
The instrument can be used to determine the salinity of sodium chloride. The salinity of sodium chloride can be used to approximate the salinity of the solution being measured. By measuring the conductivity of the sample, the mass percentage of the corresponding sodium chloride solution can be calculated to convert the sodium chloride salinity.Users can switch the measurement parameter to salinity measurement by pressing the Conductivity/TDS measurement box on the screen. The detail refers to the measurement method of conductivity salinity measurement.
5.10 Resistivity Measurement
Resistivity and conductivity are reciprocal to each other, and conductivity can be measured at the same time when measuring resistivity.Users can switch the measurement parameter to resistivity measurement by pressing the Conductivity/TDS measurement box on the screen. The detail refers to the measurement method of conductivity measurement.
5.11 Dissolved Oxygen Measurement
5.11.1 Calibration Preparation
5.11.1.1 PreparationZero oxygen is calibrated using a freshly formulated 5% sodium sulfite solution as oxygen-free water.
5.11.1.2 Electrodes preparation
When the DO electrode (polarographic) is used for the first time or has not been used for a long time, the filling solution needs to be replaced.
Follow the below instruction to replace the filling solution:
Take the cap off the electrodes, rinse the cap with DI water and dry out. Rinse the inner electrode with DI water and dry the electrode. Add the filling solution (electrolyte) into the membrane cap up to 3/4. Install the cap onto the electrode.
 【TIPS】
【TIPS】Membrane: The most important part, can't be damaged or lead to incorrect measurement. Electrolyte: Needs to be replaced every 2 weeks to 2 months, depending on the frequency of use.
5.11.1.3 Electrode Polarization
Polarographic DO electrodes need to be polarized before every use.
Connect the DO electrode to the meter and turn on the meter, wait for 1 hour and the electrode are auto polarized. When the electrodes are unplugged from the meter for no more than 1 hour, measurements are allowed after 25 minutes of polarization.
5.11.2 DO Calibration
The calibration process is as follows:1.Press “Calibrate” to select “DO Calibration”.
2.Place the electrode into an oxygen-free solution.
3.When the reading is stable, press “CAL Zero” to do zero oxygen calibration.
4.Rinse the electrode with DI water again, and place the probe in the upper part of a bottle filled with air-saturated (well shaken) water.
5.When the reading is stable, press “Cal Air-Sat” to do full oxygen calibration.
6.After calibration, press “Enter” to end the calibration.
 【TIPS】
【TIPS】The calibration process ends before it is completed, and the set parameters are not saved.
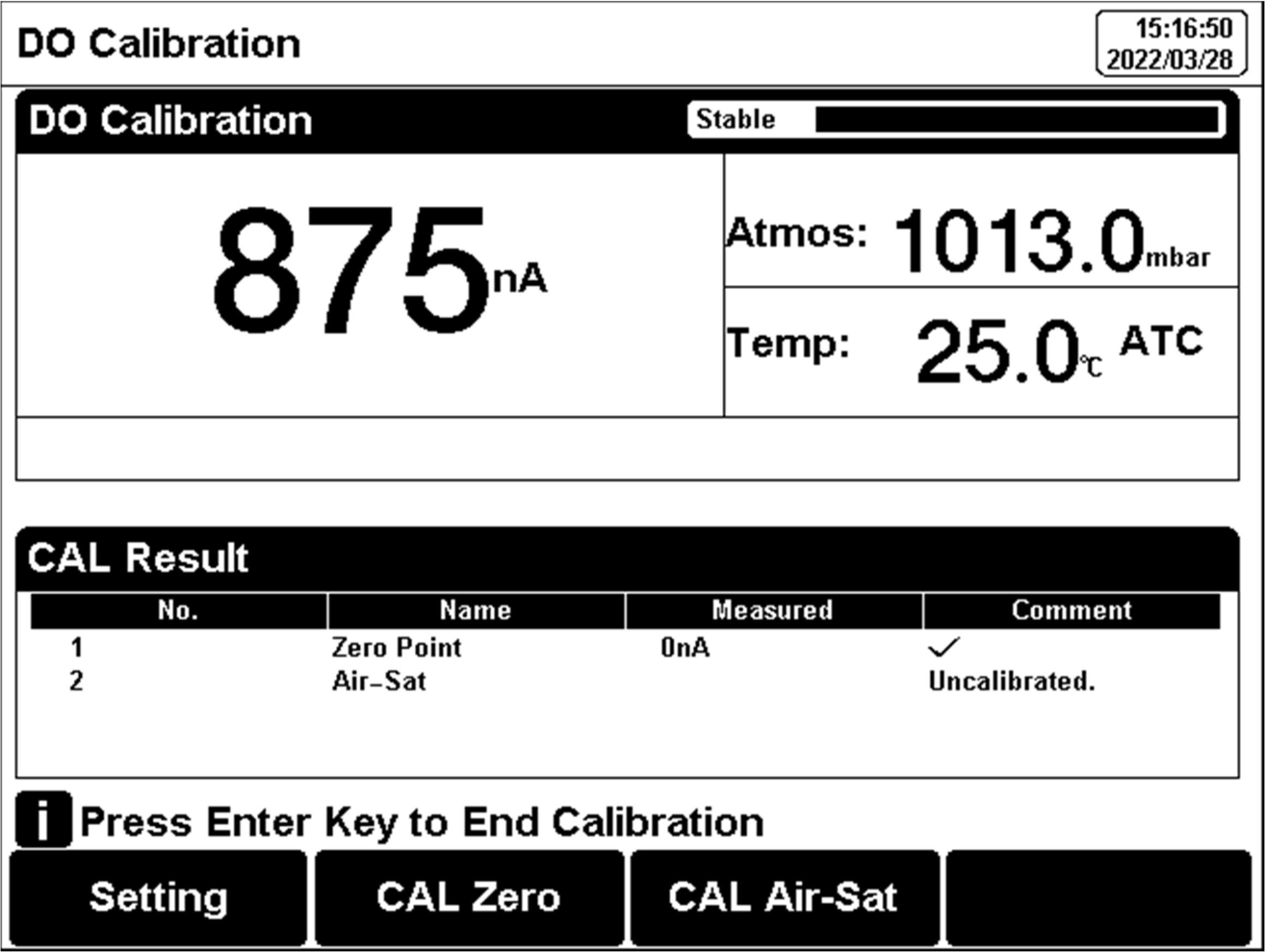
Figure 20
Dissolved oxygen calibration information
5.11.3 DO Measurement
The measurement process is as follows:1.Setting.
Set the parameters (e.g., DO). Set the reading mode (e.g., continuous reading, auto-reading, or timed format). Set the salt compensation. Set the Atmos compensation.
2.Put the electrode into the test solution under test and shake the electrode gently in a circle, in a circular motion, or use a stirrer to avoid air bubbles during the process.
3. In the idle status, press F4 "Measure" to enter into measurement status.
4. When the reading is stable, read the results.
5. Press the "Save" to save the measurement results.
6. Press the "Output" to print the measurement result when connect to the printer.
7. Between measurements, stored DO electrode in distilled or deionized water.
8. After measurement, rinse the DO electrode with deionized water thoroughly. Add the filling solution (electrolyte) into the membrane cap up to 3/4, and Install the cap onto the electrode.
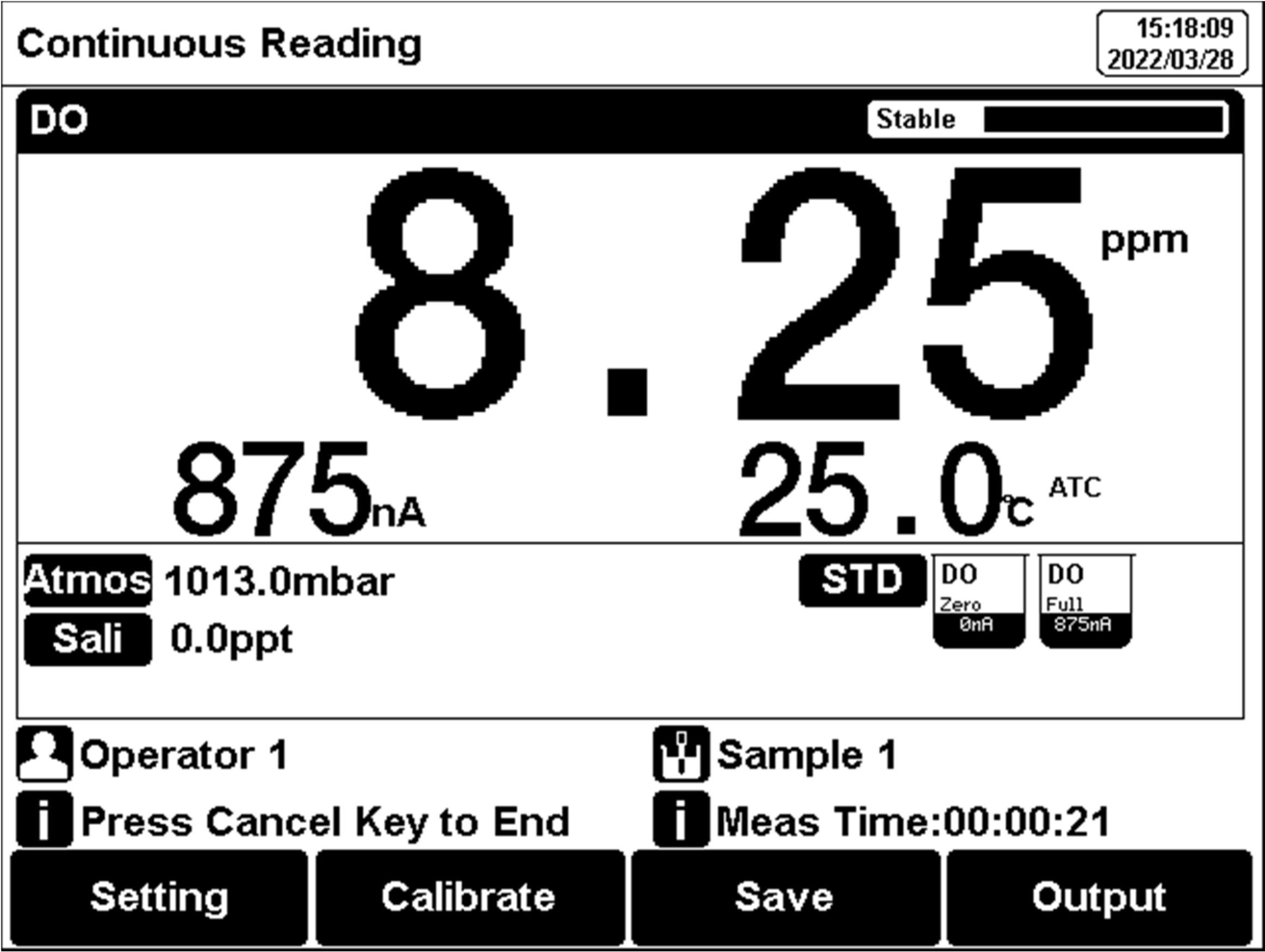
Figure 21
Dissolved oxygen measurement information.
5.11.4 DO Saturation Measurement
Dissolved oxygen saturation refers to the ratio of the dissolved oxygen concentration to the saturated dissolved oxygen concentration under the same conditions.Users can switch the measurement parameter to Saturation measurement by pressing the DO measurement box on the screen.
5.12 Data Management
Press "Data" to view the detail of the results.The meter stores the measurement results independently according to the measured parameters. The meter provides data Storage 500 sets for each parameter (pH/pX/ISE/EC/Resistivity/TDS/Salinity/DO/Saturation).
The user can press "Delete" into the delete menu. It allows users to select the current data or all data to delete.
The user can view the data filter by parameter, and locate No. or stored date. By the filter setting, press "Start Search" to look up the data. The filter data shows in a graph. Press "←" and"→" to choose data. the user can choose one and press the "Enter" key to see the detailed result. Users can press "Delete" to delete the current result. Press "Output" to select the output data. The format supports the output of the current result, output matched result, and output all results.
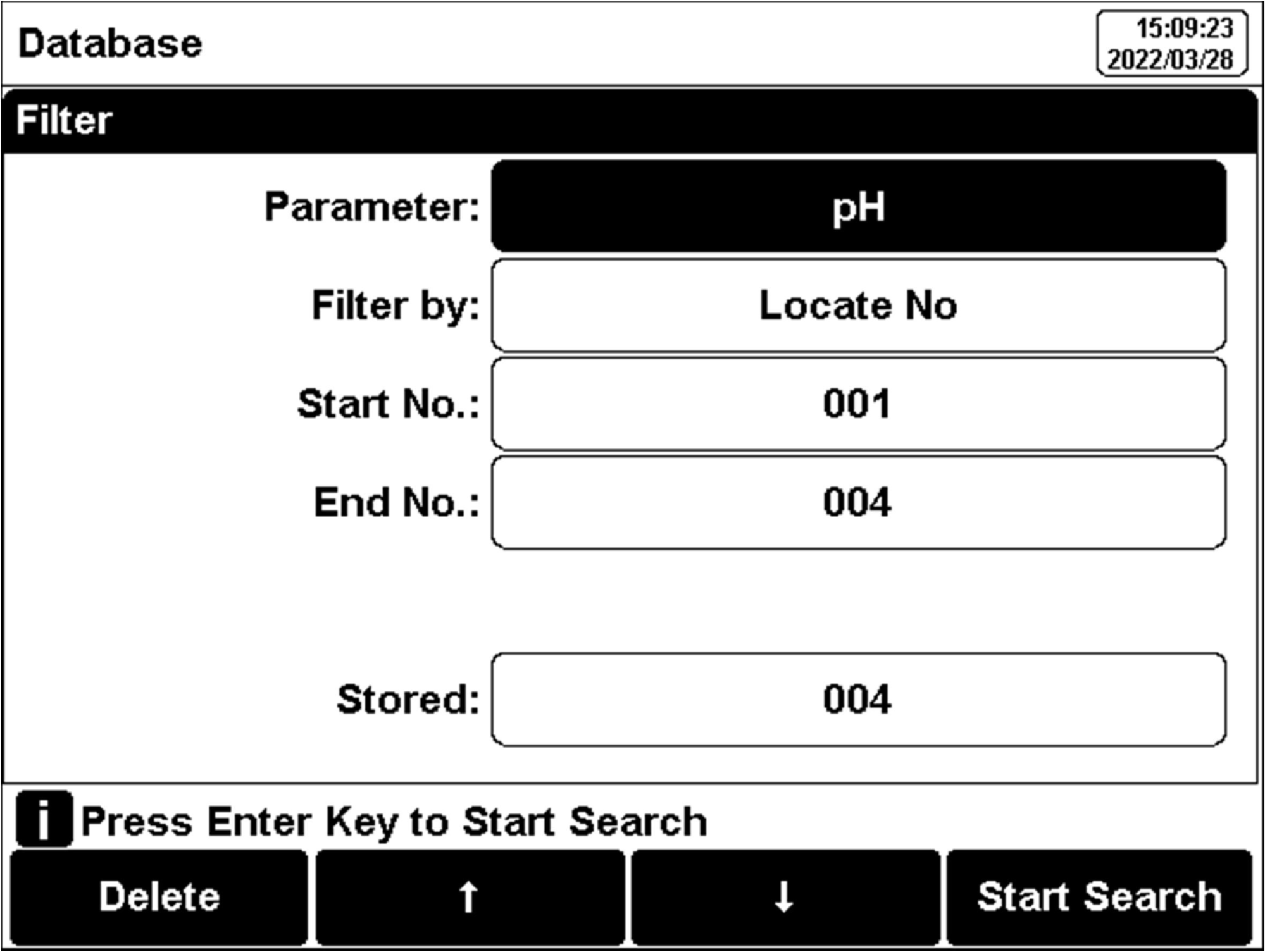
Figure 22
Results setting view
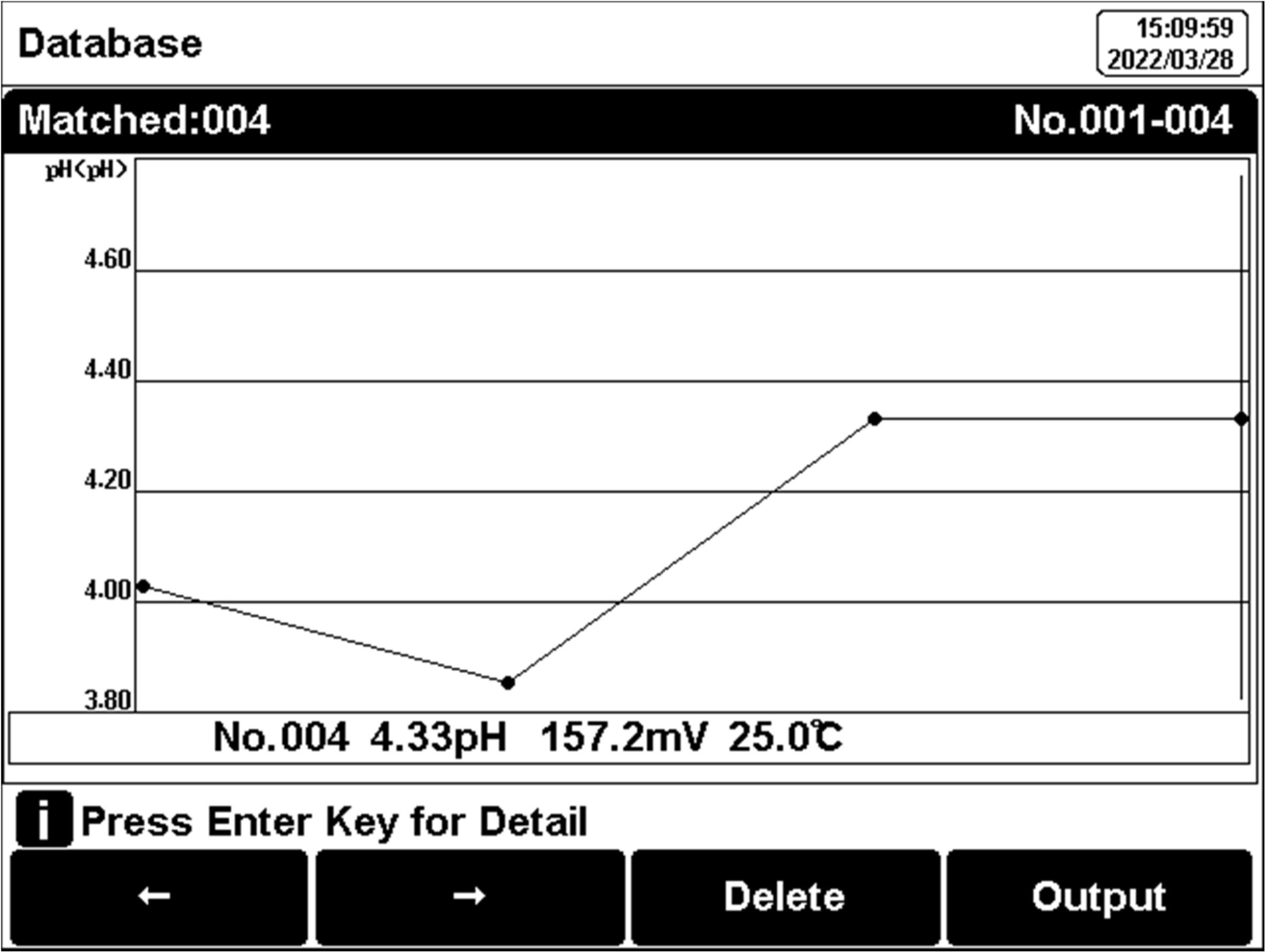
Figure 23
Results setting view
 【TIPS】
【TIPS】Please connect the meter with the printer when the meter is switched off. The Baud rate is 9600bps for printer connecting. The default setting is 8 data bits, one start bit, one stop bit, and no parity.
The output format is as followed:
Report Title
----------------------------------------
Measure Time:2021/02/06 13:31:51
Operator: Admini
Model: BMET-602 Multi-Parameter
Analyzer Serial Number:
SW Version: Ver 1.00
----------------------------------------
.............................SAMPLE INFO
Sample ID:
Sample 1
..........................ELECTRODE INFO
pH EC ID: pH Electrode
..............................CALIB INFO
Calib Operator:
REX Team Calib Time:
2020/06/18 12:13:10 Calib Num:
3
............................CALIB RESULT
STD 1: 4.01pH 176.8mV 25.0c
STD 2: 7.00pH 0.0mV 25.0c
STD 3: 10.01pH -178.1mV 25.0c
pH Slope 1:
100.00% pH E0 1:
0.0mV pH Slope 2:
100.00% pH E0 2:
0.0mV
..............................BRIEF INFO
Reading Mode: Continuous Reading
Stable Type:
Medium Temp Comp Type:
ATC
..................................RESULT
Result:
7.00pH Signal Value:
-0.2mV Temp Value:
25.0c
6. Maintenance/Troubleshooting
6.1 Meter Maintenance
The correct use and maintenance of the instrument can ensure the accurate and reliable performance of the instrument. Additionally, exposure to chemicals or harsh use environments can affect performance.The pH/pX electrode socket has a protective plug, when the meter is not in use, please insert the protective plug into the pH/pX socket.
If the meter is not used for a long time, please disconnect the power supply. The electrode socket of the instrument must be kept clean and dry, and should not be in contact with acid, alkali, and salt solutions. Keep the meter and accessories clean and away from acids, alkalis, and any corrosive solutions/gases. Users can clean the meter surface with clean water and detergent. When the meter is transported, please follow the instructions:
Please remove all connected cables. Please remove the electrode holder. Please use the original packaging in the long-distance transport to avoid damage.
6.2 Electrodes Maintenance
For more detailed information, please refer to the electrode instruction manual.6.3 Troubleshooting
Troubleshooting| Phenomenon | Probable reasons | Solutions |
| 1. No Display | Damage to the meter. | Replace or repair as required. |
| 2. Incorrect mV measurement is | The electrode is out of service life The electrode plug is in poor contact | Replace the electrodes Connect the protection plug, if the potential is not 0mV, please contact the after-sales service. |
| 3. Incorrect pH measurement | Refer to as 2.2 Refer to as 2.2 The electrodes are not calibrated or are calibrated incorrectly | Refer to as 2.2 Refer to as 2.2 Recalibrate the electrode or replace the standard solution |
| 4. Incorrect pX/ISE measurement is | Refer to as 2.2 Refer to as 2.2 The electrodes are not calibrated or are calibrated incorrectly Incorrect ISE probe | Refer to as 2.2 Refer to as 2.2 Recalibrate the electrode or replace the standard solution Buy the correct ISE probe |
| 5. Incorrect conductivity measurement | The electrode is out of service life The electrodes are not calibrated or are calibrated incorrectly | Replace the electrodes Recalibrate the electrode or replace the standard solution |
| 6. Incorrect DO measurement | The electrode is out of service life The electrodes are calibrated incorrectly Stirring speed is not good | Replace the electrodes Recalibrate the electrode Keep the bubbles in the stirring state consistent |
Table 20
If the meter still does not work, please contact your local dealer for further assistance.
7. Technical Supports
Accessories
Please refer to the accessories table for purchasing recommendations.Meter accessories
| Name | Description |
| E-301-QC 3 in 1pH composite electrode | pH Measurement Probe |
| DJS-1VTC conductivity electrode | Conductivity, TDS Measurement Probe |
| DO-958-Q dissolved oxygen electrode | Dissolved Oxygen Measurement Probe |
| Standard pH buffer solution 4.01/7.00/10.01 | Standard solution |
| Conductivity solution 1413μs/cm | Standard solution |
Table 21
8. Appendixes
Appendix 1
pH-Temperature Relationship Table of pH Standard Solutions| Temperature(°C) | 1.68 | 4.01 | 7.00 | 10.01 |
| 5 | 1.67 | 4.00 | 7.09 | 10.25 |
| 10 | 1.67 | 4.00 | 7.06 | 10.18 |
| 15 | 1.67 | 4.00 | 7.04 | 10.12 |
| 20 | 1.68 | 4.00 | 7.02 | 10.06 |
| 25 | 1.68 | 4.01 | 7.00 | 10.01 |
| 30 | 1.68 | 4.01 | 6.99 | 9.97 |
| 35 | 1.69 | 4.02 | 6.98 | 9.93 |
| 40 | 1.69 | 4.03 | 6.97 | 9.89 |
| 45 | 1.7 | 4.04 | 6.97 | 9.86 |
| 50 | 1.71 | 4.06 | 6.97 | 9.83 |
Table 22
Appendix 2
Conductivity Standard SolutionTable 1 KCl standards to electrode cell constants
| Cell constant (cm -1 ). | 0.1 | 1 | 10 |
| KCl solution Concentration (mol/L). | 0.001 | 0.01 or 0.1 | 0.1 or 1 |
Table 23
Table 2 Approximate concentrations of KCl solutions and their conductivity values (μS/cm) relationship.
| T(°C) | 84μS/cm | 1413μS/cm | 12.88mS/cm |
| 5 | 53.02 | 896 | 8.22 |
| 10 | 60.34 | 1020 | 9.33 |
| 15 | 67.61 | 1147 | 10.48 |
| 20 | 75.80 | 1278 | 11.67 |
| 25 | 84.00 | 1413 | 12.88 |
| 30 | 92,19 | 1552 | 14.12 |
| 35 | 100.92 | 1696 | 15.39 |
Table 24




